Figure 2.
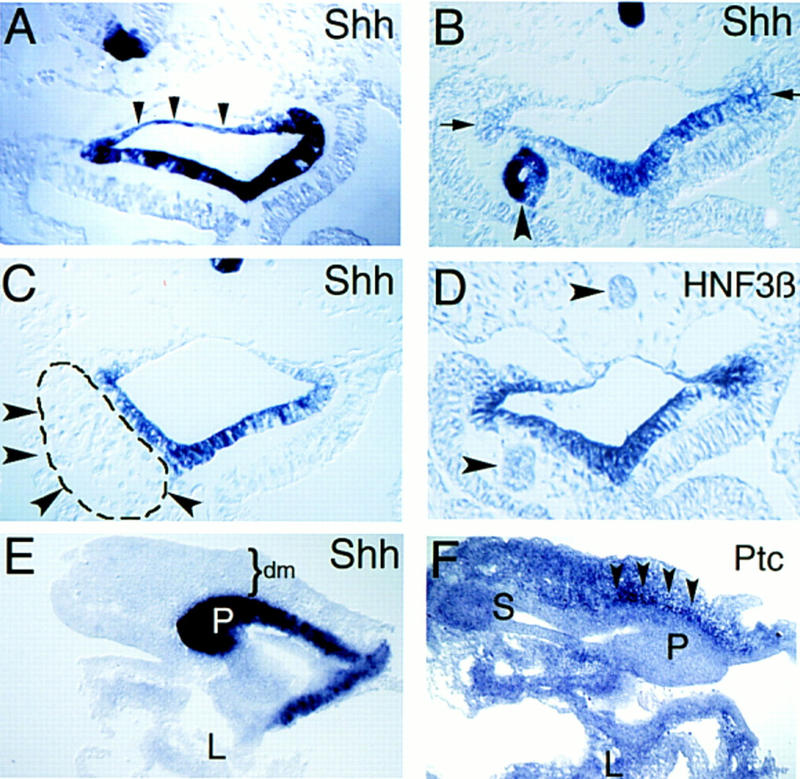
Notochord signals repress Shh expression in adjacent endoderm. Transverse sections through foregut adjacent to the anterior intestinal portal at stage 16 (A–D). (A) Ectopic Shh expression in dorsal foregut endoderm after notochord deletion (n = 10) at stage 10–11. Arrowheads outline blue dorsal endoderm. Contrast to Fig. 1B. (B) Ectopic notochord graft decreases adjacent endodermal Shh expression; compare to contralateral control side (arrows). Ectopic notochord also expresses Shh (arrowhead). The endoderm adjacent to notochord grafts is reproducibly thinner than corresponding control endoderm on the contralateral side (n = 18) The apparent lumen in the transplanted notochord is an artifact of histologic preparation. (C) Endodermal Shh expression after insertion of the ninth somite (dashed line and arrowheads), from a stage 10 donor, adjacent to endoderm. Shh expression in endoderm is unaffected compared to the contralateral side (n = 4). (D) HNF3β expression in foregut endoderm after notochord grafting. Endogenous or grafted notochord (arrowheads) does not express HNF3β at this stage. Ventral endodermal HNF3β expression is unaffected by ectopic notochord. (E,F) Sagittal sections through dissected pancreatic anlage and adjacent anterior foregut at stage 19. (E) Ectopic endodermal Shh expression in the dorsal pancreas bud (P) after notochord deletion at stage 11. Some liver (L) is seen in this section but liver and stomach endoderm are out of the section plane. Mesenchyme (dm) overlying the dorsal pancreas bud is indicated. (F) shows stomach (S), liver (L), and ectopic Ptc expression in mesenchyme (arrowheads) adjacent to the dorsal pancreas bud (P) after notochord deletion. Dorsal is toward the top; anterior is toward the left in E and F.
