Figure 3.
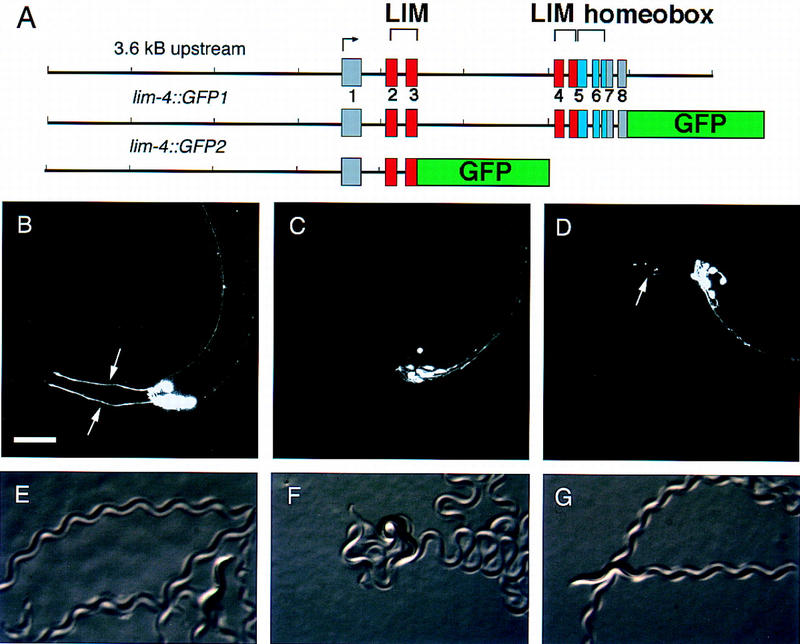
lim-4 is expressed in anterior neurons. (A) Two GFP fusion genes used to analyze LIM-4 expression. lim-4::GFP1 is a fusion of GFP to the end of the last amino acid in LIM-4, lim-4::GFP2 truncates the gene after the third exon. lim-4::GFP2 was integrated into the genome to minimize mosaicism. (B) lim-4::GFP2 expression in wild-type animals is confined to the anterior ganglia. lim-4::GFP2 is expressed in the two AWB neurons, which send dendrites to the tip of the nose (arrows), two of six RMD neurons (RMDL and RMDR), the RIV neuron, four SAA neurons, and four SIA neurons. lim-4::GFP1 is expressed in all the same cells as well as RMEV and RID (not shown). (C,D) In lim-4 mutants, AWB expression is eliminated, as is most evident by the absence of sensory dendrites. Sometimes ectopic sprouting of anterior processes from the SAA axons is visible in lim-4 mutants (D, arrow), these processes are normally unbranched. Anterior is left and dorsal is up in B–D. Scale bar, 20 μm, applies to B–D. (E–G) The full-length lim-4::GFP1 construct is capable of rescuing the lim-4 movement defect. Wild-type animals move in a characteristic manner, leaving regular, shallow sinusoidal tracks (E). lim-4 animals move in a coily manner, leaving exaggerated high amplitude tracks (F). This movement defect is rescued with a full-length lim-4::GFP1 transgene (G). The adult worms shown are ∼1 mm long.
