Figure 1.
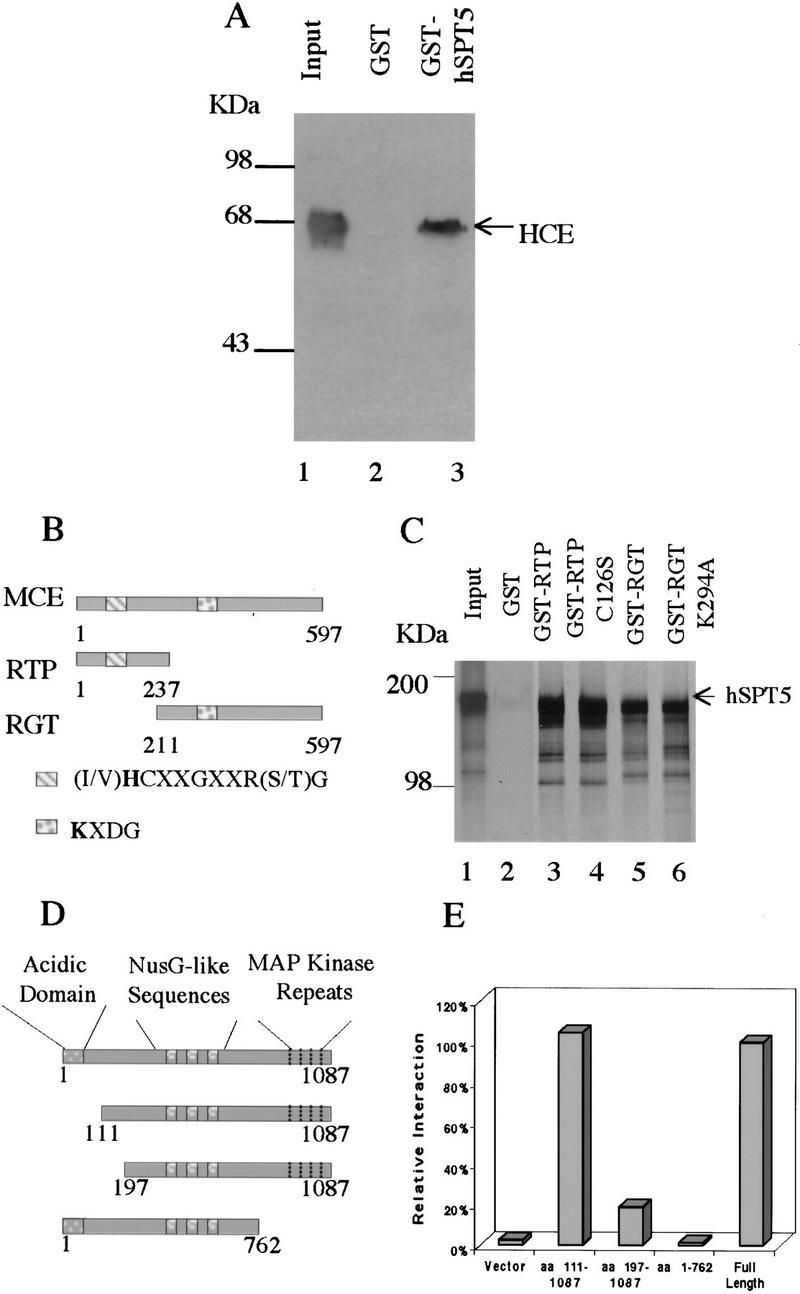
Mammalian capping enzymes interact with hSPT5 in vitro and in vivo. (A) Binding to HCE. Purified GST–hSPT5 was incubated with purified HCE (lane 1). Bound HCE was detected by SDS-PAGE followed by immunobloting with anti-MCE antisera (Yue et al. 1997; lanes 2,3) and densitometry. (Input lane) 50% of the amount of HCE used for the binding assays. (B) Schematic diagram of the MCE, RTP, and RGT domains. (C) Purified GST, GST–RTP, GST–RTP (C126S), GST–RGT, or GST–RGT (K294A) was incubated with [35S]Met-labeled hSPT5. Bound proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography. (Input lane) 10% of the amount of hSPT5 used for the assays. (D) Schematic diagram of hSPT5 protein constructs used to define sequence requirements for interaction with HCE. (E) Full-length hSPT5 and indicated truncation mutants were transformed into yeast Y190 harboring HCE. Yeast colonies that grew on SD/−Trp/−Leu were assayed for liquid β-gal activity.
