Figure 3. PD-L1 and PD-L2 cross compete for PD-1 binding.
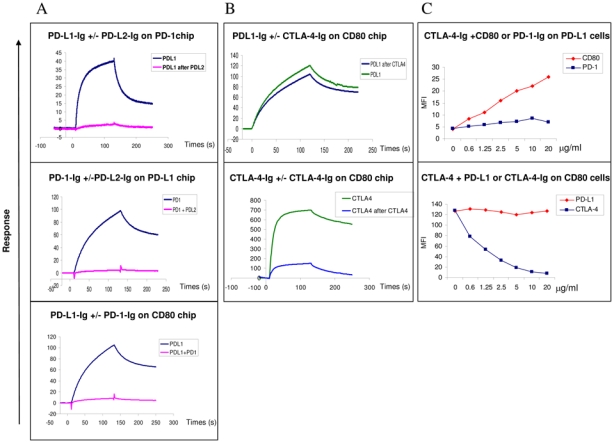
The experiments were performed using both SPR analysis using BIAcore (A and B) and flow cytometry (C)
SPR and Facs analysis PD-L1 and CTLA-4 binding to CD80
(A) Analysis by SPR of the binding of PD-L1 to PD-1 or CD80 coated on chips following preincubation with PD-L2 or PD-1 respectively. The data shown are representative of two separate experiments.
Top row: The PD-1 chips were pre-incubated twice with saturating amounts of PDL2 and PD-L1 then were injected in a third step at 10 μg/ml for 2 minutes at a flow rate of 10 μl/min without removing bound PD-L2. Sensorgrams showing the PD-L1 binding in the presence or absence of PD-L2 occupancy are superimposed. Middle row: PD-1 proteins were pre-incubated with saturating amounts of PD-L2 and the resulting complexes were injected at 10 μg/ml for 2 minutes at a flow rate of 10 μl/min onto PD-L1-Ig chips. Sensorgrams showing the PD-1 binding alone or complexed with PD-L2-Ig are superimposed.
Lower row: PD-L1-Ig proteins were pre-incubated with saturating amounts of PD-1- Ig and the resulting complexes were injected at 10 μg/ml for 2 minutes at a flow rate of 10 μl/min onto CD80-Ig chips. Sensorgrams showing the PD-L1 binding alone or complexed with PD-1 are superimposed.
(B) CTLA-4 does not to prevent the binding of PD-L1-Ig to CD80 using SPR analysis. The data shown are representative of two separate experiments. Superimposed sensorgrams representative of PD-L1 (top row) and CTLA-4 (lower row) binding to CD80-Ig chips following or not pre-incubation with CTLA-4-Ig. The CD80 chips were pre-incubated twice with saturating concentrations of CTLA-4- Ig, then in a third step PD-L1-Ig or CTLA-4-Ig used at 10 μg/ml were injected for 2 minutes at a flow rate of 10 μl/min onto CD80-Ig chip and allowed to dissociate for 2 more minutes
(C) CTLA-4 and PD-L1 bind together to CD80 on the cell surface Top row: CTLA-4-Ig can bind to PD-L1 expressing COS cell in presence of CD80 but not PD-1. Biotinylated CTLA-4-Ig protein at 2 μg/ml was incubated with CD80- Ig or PD-1-Ig proteins (from 0 to 20 μg/ml) before addition to PD-L1 expressing cells. The binding of biotinylated CTLA-4 proteins were revealed with StreptAvidin-conjugated with PE, the MFI was indicated in the Y axis. The data shown are representative of three separate experiments.
Lower row: CTLA-4-Ig can bind to CD80 expressing cells in presence of PD-L1-Ig. Biotinylated CTLA-4-Ig at 2 μg/ml was incubated with increasing concentrations of PD-L1-Ig or CTLA-4-Ig (from 0 to 10 μg/ml) before addition to the CD80+ Raji cell. The binding of biotinylated CTLA-4-Ig was detected using StreptAvidin-conjugated with PE, the MFI was indicated in the Y axis. The data shown are representative of three separate experiments.
