Figure 1.
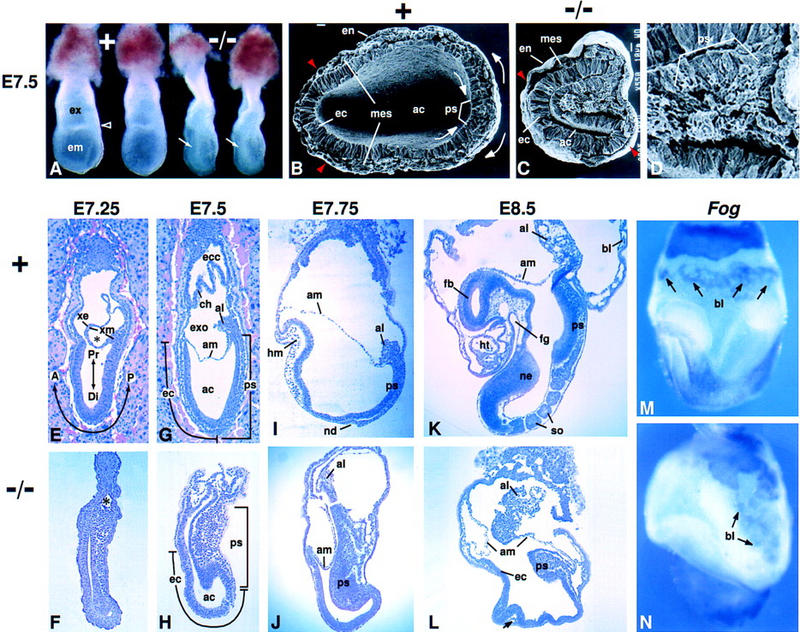
Morphology of Fgf8−/− embryos. In all figures, anterior is to left and posterior to right; intact embryos are viewed laterally, unless otherwise noted. The genotype of each embryo is indicated: Normal embryos were either Fgf8+/− or Fgf8+/+. (A) Offspring at E7.5 of a cross between Fgf8+/− mice. A characteristic bulge of cells in the amniotic cavity (arrow) identifies the two embryos at right as mutant homozygotes. The open arrowhead points to the border between the embryonic (em) and extraembryonic (ex) regions in a normal littermate. (B–D) Scanning electron micrographs of the embryonic region at E7.5. (B) Arrows indicate the direction of epiblast cell movement toward the primitive streak and of mesoderm cell migration away from the streak in a normal embryo. The transverse plane of section was somewhat oblique (higher at right). (C) Fgf8 mutant embryo illustrating the distortion of the primitive streak region, which bulges into the amniotic cavity. Embryos in B and C are shown at the same magnification. (B,C) Red arrowheads indicate the most anterior extent of mesoderm cell migration away from the streak. (D) Higher magnification view of the primitive streak region of the embryo shown in C. Note the accumulation of cells with mesenchymal morphology. (E–L) Sagittal sections of normal and mutant embryos; E and G show embryos sectioned in utero. The times at which they were collected are indicated. The A-P and P-D axes are indicated in E. (E,F) Mid-streak-stage embryos. (*)The nascent exocoelom, which consists of a layer of extraembryonic ectoderm and a layer of mesoderm. (G,H) Late-streak-stage embryos. The extent of the primitive streak and the anterior ectoderm (prospective neuroectoderm) is indicated. (I,J) The normal embryo is at the head-fold stage. In a mutant embryo collected at the same stage, head mesenchyme and a morphologically distinct node are absent. (K,L) The normal embryo contains several somites, a heart, and foregut; the mutant embryo does not contain any such mesoderm- or endoderm-derived tissues. The arrow in L points to a small, isolated patch of mesodermal cells in the mutant embryo. (M,N) Whole-mount in situ hybridization assay for Fog RNA in E8.5 embryos. Signal is detected in blood islands (arrows). (A) Anterior; (ac) amniotic cavity; (al) allantois; (am) amnion; (bl) blood island; (ch) chorion; (Di) distal; (ec) anterior ectoderm (prospective neuroectoderm); (ecc) ectoplacental cone; (em) embryonic region; (en) endoderm; (ex) extraembryonic region; (exo) exocoelom; (fb) forebrain; (fg) foregut; (hm) head mesoderm; (ht) heart; (mes) mesoderm; (nd) node; (ne) neuroectoderm; (P) posterior; (Pr) proximal; (ps) primitive streak; (so) somite; (xe) extraembryonic ectoderm; (xm) extraembryonic mesoderm; (+) normal; (−/−) mutant.
