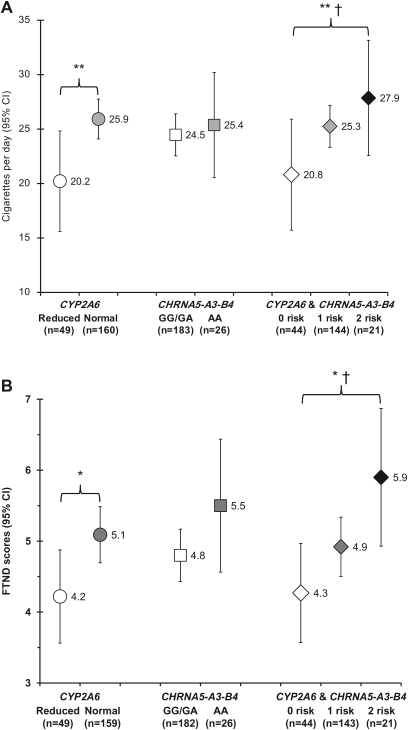
Figure 1.
Association of CYP2A6 and CHRNA5-A3-B4 genotype with smoking behaviors. A) Self-reported cigarettes smoked per day and B) Fagerström Test for Nicotine Dependence (FTND) scores are displayed for control subjects who were current smokers and are shown as the mean with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) by genotype group. The genotypes analyzed include the CYP2A6 genotype alone, the CHRNA5-A3-B4 genotype alone, and the combined CYP2A6 and CHRNA5-A3-B4 genotype groups according to the number of risk genotypes. The low-risk group (0 risk) included CYP2A6 reduced metabolizers with the CHRNA5-A3-B4 GG and GA genotypes. The intermediate-risk group (one risk) included participants with either the CYP2A6 normal metabolizer genotypes or the CHRNA5-A3-B4 AA genotype, and the high-risk group (two risk) included CYP2A6 normal metabolizers with the CHRNA5-A3-B4 AA genotype. P values were calculated by Kruskal–Wallis tests. *P < .05, **P < .001. Ptrend was calculated by a generalized linear model. †Ptrend < .05. All statistical tests were two-sided.