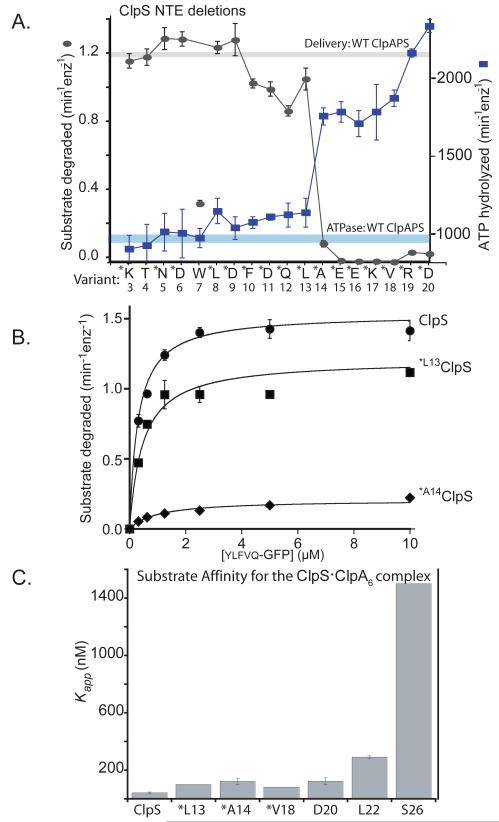
Figure 4. A minimal NTE length is required for ClpS function.
A) ClpS variants (1 μM) with N-terminal truncations were assayed for delivery of ylfvqela-GFP (1 μM) for ClpAP degradation (gray curve) and for effects on ClpAP ATP hydrolysis (blue curve) using 100 nM ClpA6 and 270 nM ClpP14 for both assays. Data points represent averages (n=3) ± 1 SD. Each ClpS variant is named by the first wild-type residue in the construct. Those marked with an asterisk contain an additional N-terminal methionine and are therefore one residue longer than the labels indicate; these mutants were expressed as SUMO-fusion proteins and cleaved in vitro (see Experimental Procedures) or were expressed as standard non-fusion proteins but retained the initiator Met (verified by mass spectrometry). The T4 and W7 variants were also expressed as standard non-fusion proteins but mass spectrometry and/or N-terminal sequencing showed that the initiator Met was removed from both of these proteins. Note the sharp activity transitions between *L13 ClpS (starting Met12Leu13) and *A14 ClpS (starting Met13Ala14). The processing of the W7 variant is inconsistent with canonical methionine aminopeptidase activity and generates a good N-end-rule residue, which may be responsible for the poor activity of this ClpS variant in delivering other N-end-rule substrates.
B) Michaelis-Menten plots of ylfvqela-GFP degradation by ClpAP and ClpS or variants (100 nM ClpA6; 200 nm ClpP14; 600 nm ClpS or variants). Wild-type ClpS and *L13 ClpS (beginning Met12Leu13Ala14) supported roughly similar steady-state degradation kinetics, but delivery by *A14 ClpS (beginning Met13Ala14Glu15) resulted in a substantial decrease in Vmax. Thus, the NTE must have a critical minimal length to support efficient substrate delivery. The solid lines are a global fit to a model in which the ClpS-substrate complex binds ClpA in an initial bimolecular step (K1 = 1.1 μM) and then is engaged for degradation in a second unimolecular step (K2), which depends on NTE length. In this model, apparent Vmax = Etotal•kdeg/(1+K2) and apparent KM = K1•K2/(1+K2). For the fits shown, the kdeg value was 2.1 min−1 and the K2 values were 0.37 (wild-type ClpS), 0.74 (*L13 ClpS), and 9.2 (*A14 ClpS).
C) Binding to an N-end-rule peptide (LLYVQRDSKEC-fl; 150 nM) by complexes of ClpA6 with ClpS variants (1 ClpS per ClpA6) showed that ClpS junction residues are important for formation of the high-affinity delivery complex. Variants marked * have an additional N-terminal methionine. Apparent affinity constants were 43 nM (wild-type ClpS), 100 nM (*L13), 130 nM (*A14), 83 nM (*V18), 130 nM (D20), 290 nM (L22), and 1500 nM (S26).