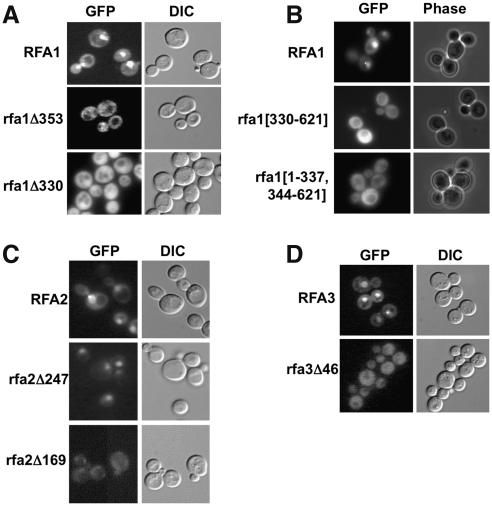
FIG. 2.
Functional alleles of RPA localize to the nucleus, whereas nonfunctional truncations do not. (A) RFA1-GFP fusions under control of their endogenous promoter were expressed in wild-type cells and localized by fluorescence microscopy (GFP) and DIC microscopy of live cells. Rfa1-GFP localized predominantly to the nucleus, whereas the truncations remained in the cytosol. (B) Full-length RFA1-GFP and rfa1 deletion mutants under control of the GAL1 promoter were induced for 2 h with 2% galactose and examined for intracellular localization. RFA1-GFP is primarily in the nucleus, whereas deletion mutants lacking residues 338–343 or 1–329 are retained within the cytoplasm. (C, D) Full-length and truncated RFA2-GFP and RFA3-GFP fusions were expressed in live cells and examined by live cell microscopy. For Rfa2, the full-length protein and the functional rfa2Δ247-GFP fusion localized to the nucleus, whereas the nonfunctional rfa2Δ169-GFP did not. Rfa3-GFP was efficiently imported into the nucleus, whereas the fusion encoded by the rfa3Δ46 truncation remained primarily cytosolic. DIC, differential interference contrast; RPA, replication protein A.