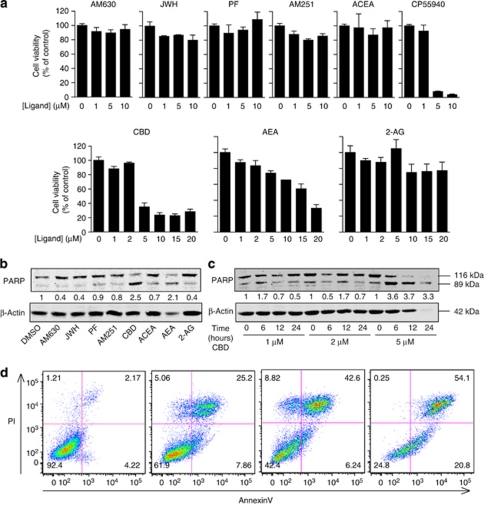
Figure 1.
CBD induces apoptosis in activated HSCs. (a) Cell viability of activated rat HSCs was determined using an acid phosphatase assay following serum starvation and 8-h treatment with indicated concentrations of cannabinoid ligands. Cell survival is presented as percent of acid phosphatase activity in vehicle-treated cells, expressed as mean±S.E.M. of triplicate experiments. AM630, CB2R antagonist; JWH (JWH133), CB2R agonist; PF (PF514273), CB1R antagonist; AM251, CB1R antagonist; ACEA, CB1R agonist; CP55940, CB1R/CB2R agonist; AEA, endogenous CB1R/CB2R agonist; 2-AG, endogenous CB1R/CB2R agonist. (b) Cell death was determined by western blot analysis of cleaved PARP in activated-rat HSCs, following 12-h incubation in serum-free media in the presence of either vehicle (DMSO) or 5 μM of indicated cannabinoid ligands. PARP cleavage is expressed as cleaved PARP over total PARP. (c) PARP cleavage was examined as in (b) in activated rat HSCs treated with CBD for the indicated concentrations and time periods. Western blots are representative of n=three experiments. (d) Activated rat HSCs were incubated in serum-free media in the absence or presence of 5 μM CBD for 2, 4, and 8 h, then stained for FITC-Annexin V and propidium iodide (PI). Cells were sorted and analyzed by flow cytometry. The percentage of cells that are either negative or positive for Annexin V and/or PI is indicated in the appropriate quadrant of each panel