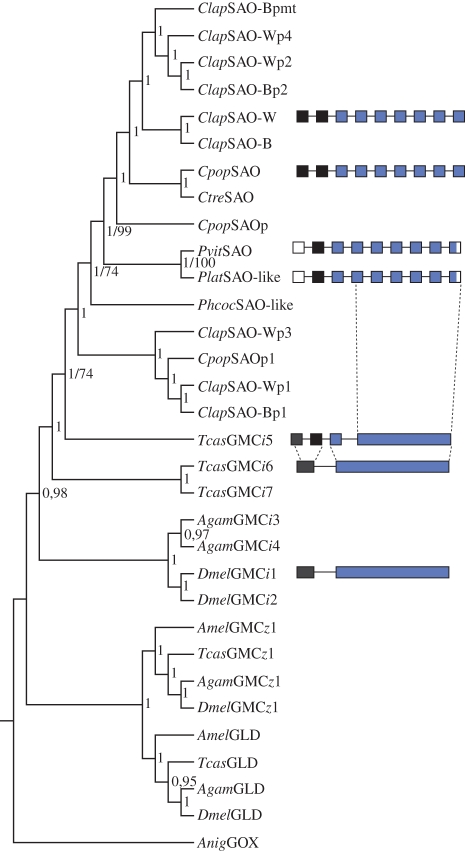
Figure 6.
Phylogeny of chrysomeline SAOs and related GMC oxidoreductases, including other insects. The topology was generated using a Bayesian analysis. Posterior probability values are shown next to each node. Bootstrap values are exemplary stated as second numbers (for details of parameters and sequence information, see §2 and electronic supplementary material, table S3). Chrysomeline SAO and other insect GMCi gene architectures are depicted next to the phylogenetic tree. Exons are shown with boxes, the same colour coding indicates common origin among different species, empty boxes mark gaps in our dataset and the dashed lines mark intron accumulations. Clap (C. lapponica), Cpop (C. populi), Ctre (C. tremulae), Pvit (P. vitellinae), Plat (P. laticollis), Phcoc (Phaedon cochleariae), Tcas (T. castaneum), Anig (Aspergillus niger), SAO-W/B (salicyl alcohol oxidase of willow/birch-feeder), GMC (glucose–methanol–choline oxidoreductase), GLD (glucose dehydrogenase), GOX (glucose oxidase), p (SAO paralogues), pmt (SAO paralogues Malpighian tubule specific).