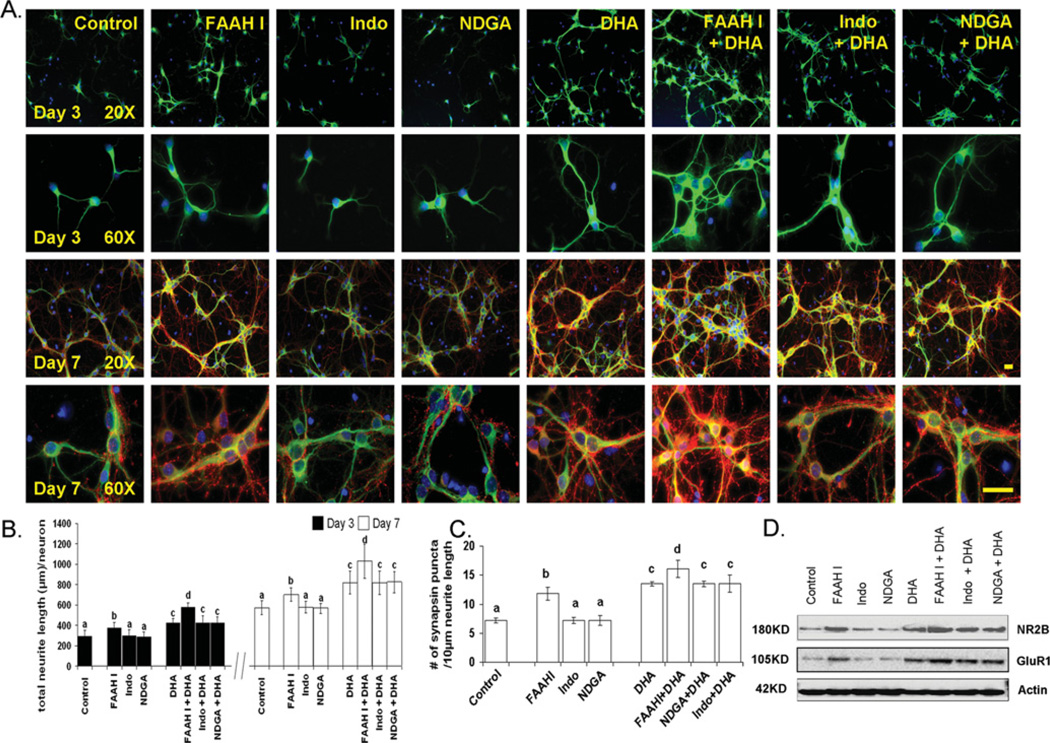
Figure 1. Effect of inhibitors of fatty acid metabolism on hippocampal development.
Although indomethacin (Indo, 50 µM) and NDGA (10 µM) exerted no effects, inhibition of FAAH using URB597 (1 µM, FAAHI) enhanced neurite growth at 3 and 7 DIV (days in in vitro culture) (B) as well as synapsin puncta formation (C) and NMDA receptor expression at 7 DIV (D). (A) Representative photomicrographs of E18 mouse hippocampal neurons after culturing for 7 days in the presence of various inhibitors: MAP2 (a neuron-marker protein) green; synapsin-1, red; and DAPI (for nuclei), blue. Scale bars, 30 µm. (B and C) Quantitative changes in neurite growth (B) and synaptogenesis evaluated by the number of synapsin puncta/10 µm of neurite (C). Statistical analysis was performed by post-hoc Tukey’s HSD tests at the significance level of P < 0.05. Different alphabetical letters indicate statistically significant differences. (D) Western blot analysis for NR2B expression.