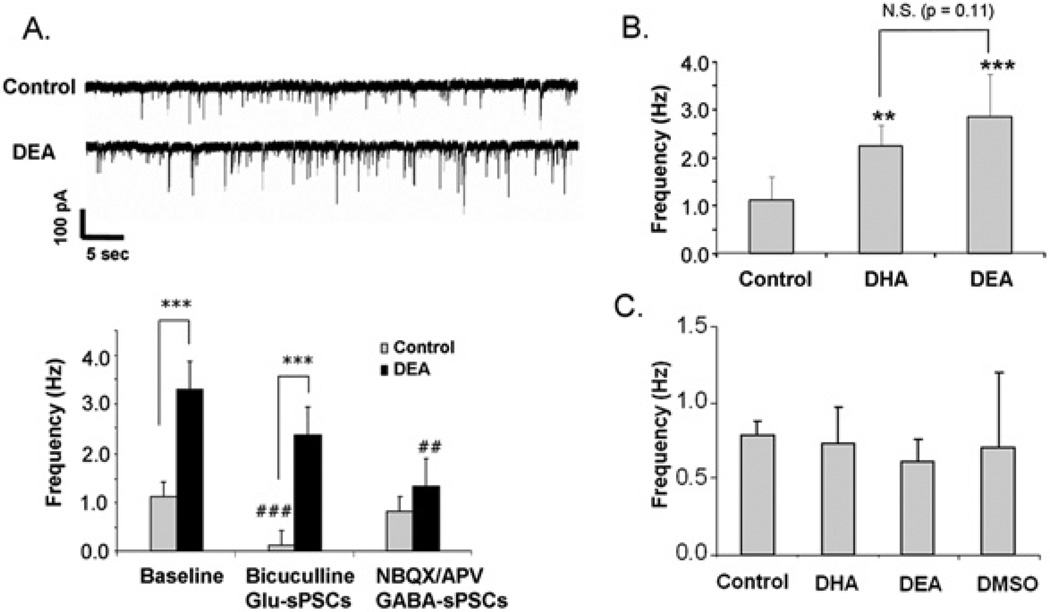
Figure 7. Effects of DEA on synaptic activity.
(A) sPSCs, including Glu-sPSC and GABA-sPSC components, in hippocampal neurons cultured with or without 0.1 µM DEA for 10 days. DEA-supplemented neurons exhibited increased frequency of sPSCs. The frequency of sPSCs in unsupplemented control neurons was decreased significantly by bicuculline, whereas NBQX/APV decreased the frequency in the DEA-supplemented neurons. Upper panel: representative sPSC traces obtained from control and DEA-treated neurons. Paired Student’s t tests were performed against the baseline value of each group (##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001) or between indicated groups (***P < 0.001). (B) sPSCs in hippocampal neurons supplemented with 1 µM DHA or 0.1 µM DEA for 10 days. Paired Student’s t tests were performed against the control value (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). (C) No effects of acute application of DHA or DEA on synaptic activity. Error bars represent S.E.M. (n = 5). The data represent three independent experiments. N.S., not significant.