Figure 2.
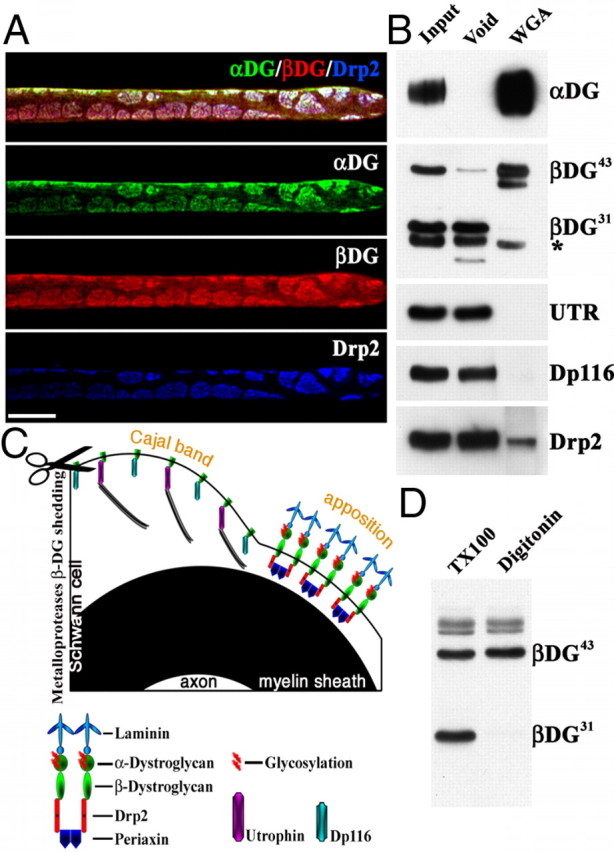
β-DG43 and β-DG31 copurify with different intracellular partners. A, Triple immunofluorescence staining of teased fibers from adult mouse sciatic nerves using antibodies against α-DG (green), β-DG (red), and Drp2 (blue). Confocal microscopy was used to detect the signal from the most superficial layer of the Schwann cell plasma membrane. Costaining shows colocalization of Drp2 and α-DG in apposition/patches and absence of α-Dg in Cajal bands. Scale bar, 10 μm. B, WGA pull-down from adult sciatic nerves. Most β-DG43 is detected in the WGA fraction, whereas β-DG31 is only present in the void fraction (* marks an Ig nonspecific band recognized by the secondary antibody; see Material and Methods). The only dystrophin in the WGA fraction is Drp2, utrophin (UTR), and Dp116 are in the void fraction. C, Proposed model of the localization of different dystroglycan complexes in Schwann cells. β-DG31 is cleaved by MMP-2/9 (scissor) and associates with utrophin or Dp116 in Cajal bands. Uncleaved β-DG43 associates with α-DG extracellularly, Drp2 and periaxin intracellularly, and localizes at appositions. D, Western blot of adult sciatic nerve shows extraction of β-DG31 with 1% Triton X-100 but not with 1% digitonin.
