Figure 4.
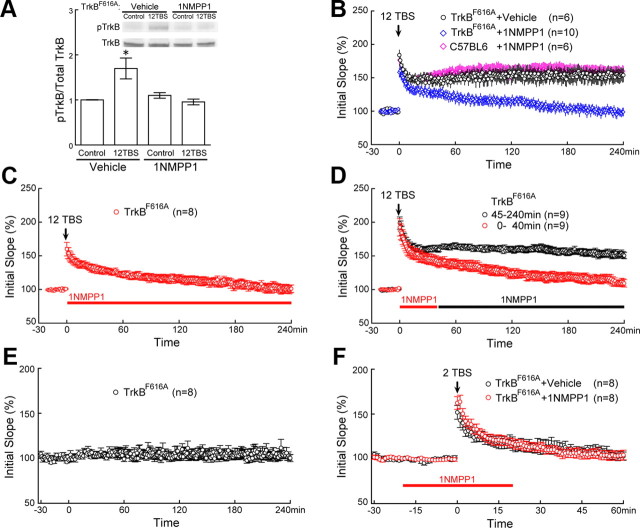
Critical role of TrkB activation within the first 40 min of L-LTP, but not in STP. A, 1NMPP1 blocked 12TBS-induced TrkB activation in TrkBF616A mice. The CA1 regions of hippocampal slices from TrkBF616A mice were microdissected 1 h after 12TBS. For each experiment, three mice were used, and for each condition, four CA1 slices were used. The same experiment was repeated five times (n = 5), each with new batch of animals. 1NMPP1 (5 μm), but not vehicle control (DMSO), blocked the 12TBS-induced increase of pTrkB in TrkBF616A mice (*p < 0.003; one-way ANOVA). B, Blockade of 12TBS induced L-LTP by inhibiting TrkB activation with 1NMPP1 in adult hippocampal slices derived from TrkBF616A mice. 1NMPP1 (5 μm), applied to slices throughout the experiment, completely blocked L-LTP (blue diamonds), while vehicle control had no effect (black circles). 1NMPP1 did not affect L-LTP in the control mice (C57BL/6) (pink diamonds). C, 1NMPP1 applied immediately after 12TBS also blocked L-LTP in TrkBF616A slices. D, Inhibition of L-LTP by 1NMPP1 applied between 0 and 40 min after 12TBS (red) but not 45 min after 12TBS in TrkBF616A slices (black). E, Stable baseline recording were obtained for >4 h without any treatment. F, Indistinguishable STPs in 1NMPP1- and vehicle-treated TrkBF616A slices. STPs were induced by 2TBS. In both cases, fEPSPs returned to baseline at 60 min after 2TBS.