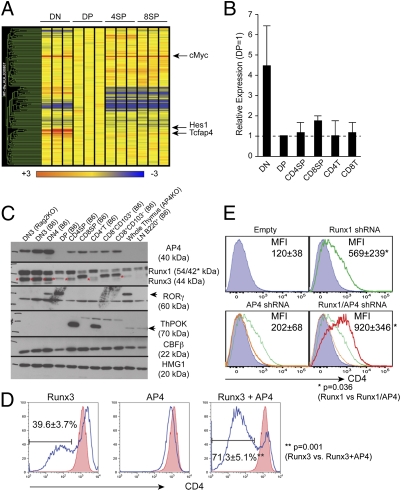
Fig. 1.
Identification of AP4 as a Cd4 silencing factor. (A) Microarray analysis of genes encoding bHLH domain-containing proteins in different thymocyte subsets. Relative signal intensity is normalized against the expression level in DP thymocytes (shown as yellow). (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of AP4 (Tcfap4) expression. Values were normalized against Hprt1 expression levels and are shown relative to the DP expression level. Data represent the average and SD of two independently prepared samples for each cell type. (C) Western blotting analysis of AP4 expression in different subsets of thymocytes and mature T lymphocytes. Anti-Runx, -RORγt, -ThPOK, and -CBFβ immunoblots serve as controls for population purity, and anti-HMG1 serves as a loading control. (D) Effect of AP4 overexpression in a double-positive thymoma cell line. AP4 and/or Runx3 were retrovirally expressed in AKR1 cells, and CD4 expression was assessed in transduced cells at 72 h postinfection (blue lines). Red-filled histograms indicate CD4 expression in empty virus-transduced controls. Proportions of CD4lo/– cells are shown with averages and SDs from five experiments. (E) AP4 and Runx1 synergistically regulate active Cd4 silencing in the 1200M cell line. CD4 expression in cells transduced with shRNAs targeting AP4 (orange), Runx1 (green), or both (red). Mean fluorescence intensities of CD4 staining are shown with averages and SDs from five experiments. Statistical significance was tested by unpaired two-tailed t test with P values shown.