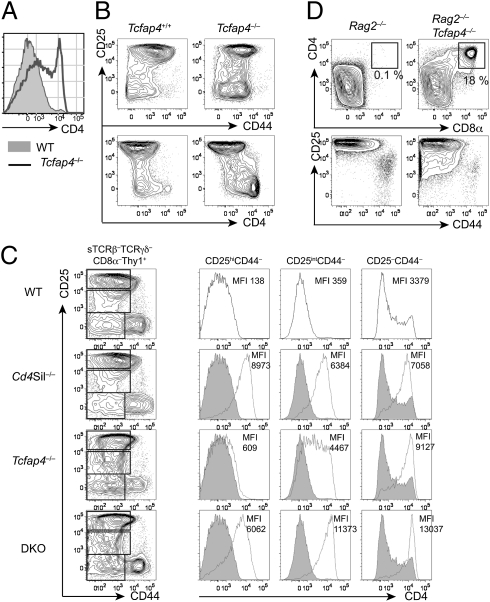
Fig. 2.
AP4 is required for Cd4 silencing in immature thymocytes. (A) CD4 expression in sTCRβ–TCRγδ–CD8α–Thy1+ thymocytes from AP4-deficient (open histogram) and WT control (filled histogram) mice. (B) CD4 is robustly up-regulated following β selection in AP4-deficient thymocytes. CD4, CD25, and CD44 expression of sTCRβ–TCRγδ–CD8α–Thy1+ thymocytes from AP4-deficient and WT control mice. (C) AP4 synergizes with Cd4 silencer-binding factors to repress CD4 in immature thymocytes. CD4 expression in preselection DN3 cells (CD25hiCD44–), postselection DN3 cells (CD25intCD44–) and DN4 cells (CD25–CD44–) from WT (black lines in the top row and filled histograms), Cd4 silencer-deficient mice (Cd4Sil−/−), AP4-deficient mice (Tcfap4−/−), and mice doubly deficient for the Cd4 silencer and AP4 (DKO) is shown in histograms with mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) indicated. Data shown here are representative of more than three independent experiments. Statistical analysis is shown in Fig. S5C. (D) AP4 deficiency allows Rag2-deficient thymocytes to bypass β selection. CD4, CD8α, CD25, and CD44 expression in Thy1+ thymocytes from Rag2−/− or Rag2−/−Tcfap4−/− mice is shown.