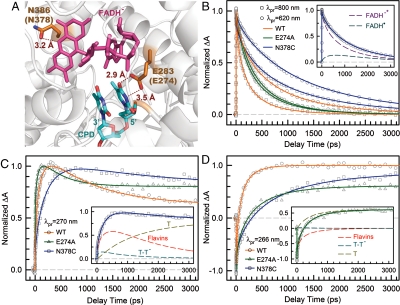
Fig. 4.
Effect of active-site mutations on repair dynamics. (A) X-ray structure of the active site of A. nidulans photolyase with two critical residues of N386 (N378 in E. coli) and E283 (E274 in E. coli). The hydrogen-bonding distances of the two residues with FADH- and CPD are also shown, respectively. (B–D) Femtosecond-resolved absorption signals of the repair of damaged CPD by the wild type and two mutants (N378C and E274A) probed at 800 and 620 nm (B), 270 nm (C), and 266 nm (D). Insets in (B) and (C) show the deconvolution of various species’ contributions of N378C mutant probed at 620 and 270 nm, respectively, while the inset in (D) for E274A mutant probed at 260 nm.