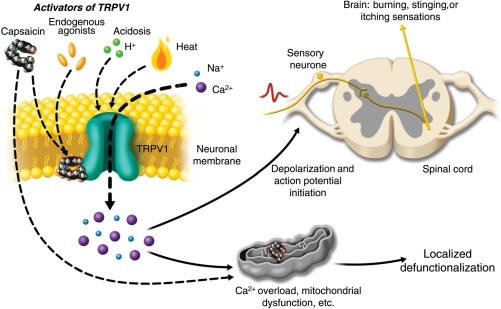
Fig 2.
Activation of TRPV1 by capsaicin results in sensory neuronal depolarization, and can induce local sensitization to activation by heat, acidosis, and endogenous agonists. Topical exposure to capsaicin leads to the sensations of heat, burning, stinging, or itching. High concentrations of capsaicin or repeated applications can produce a persistent local effect on cutaneous nociceptors, which is best described as defunctionalization and constituted by reduced spontaneous activity and a loss of responsiveness to a wide range of sensory stimuli.