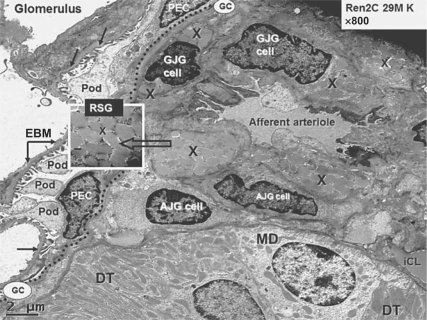
Fig. 1.
Juxtaglomerular apparatus depicting RSG. This transmission electron micrograph from a young transgenic Ren2 rat model of hypertension and insulin resistance demonstrates the renal glomerulus separated by Bowman's glomerular capsule (GC; dotted line) from the adjacent juxtaglomerular apparatus, which includes the afferent arteriole, the distal tubule (DT), which bisects the afferent and efferent arterioles in each nephron containing the macula densa (MD) cell(s). The afferent arteriole demonstrates the granular juxtaglomerular cells (GJG) containing RSG (X) and agranular or depleted juxtaglomerular (AJG) cells. Inset depicts RSG at higher magnification (open arrow; ×8,000; bar = 200 nm). Note the visceral epithelial cell(s) termed podocyte(s) (Pod) with their cytoplasmic processes and parietal epithelial cells (PEC) at the periphery of the glomerulus and the podocyte foot processes adhering to the endothelial basement membrane (EBM; closed arrows) within the glomerulus. The interstitial capillary lumen (iCL) in the lower right-hand side of the image is thought to be the major site of renin absorption and subsequent delivery to the systemic circulation.