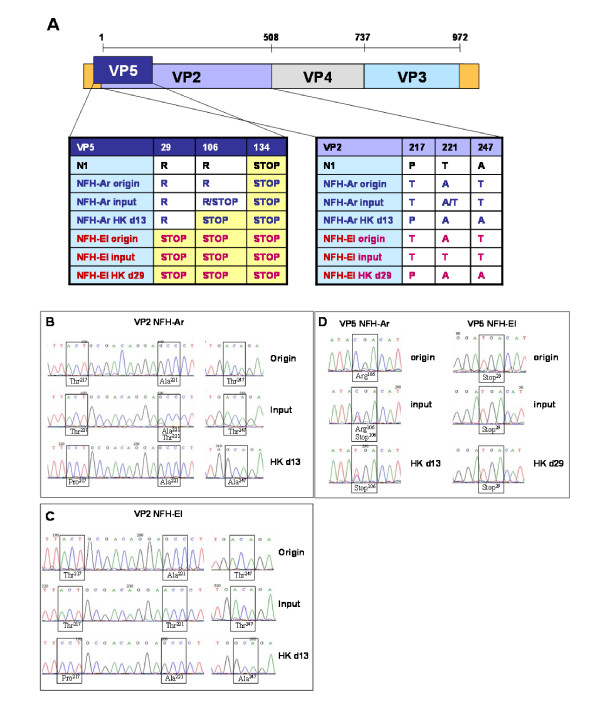
Figure 3.
Sequence analyses of IPNV segment A. A. A schematic presentation of the IPNV genome segment A which encode VP2, VP4, VP3 and VP5. Positions of divergent amino acid are indicated, and the sequences of VP2 and VP5 from the two field isolates NFH-Ar and NFH-El are compared to the non-virulent lab-strain N1 before and after the challenge experiment. B. Sequencing chromatograms showing that amino acids in positions 217, 221 and 247 of VP2 were changing rapidly in cell culture and in challenged fish. The PCR-products sequenced from the NFH-Ar strain changed partially from a TAT motif found in the originally infected fish (origin) to a TTT motif after propagation in CHSE-214 cells for the challenge experiment (input). Virus isolated from the fish after the challenge had a PAA motif (HK d13). C. The NFH-El strain changed from a TAT found in the original material (origin) to a TTT motif after three passages in CHSE-214 cells (input). Virus isolated from the fish after this challenge (HK d29) had a PAA motif like seen in the NFH-Ar challenged fish. D. The ORF of VP5for the NFH-Ar strain changed from a 133 amino acid peptide to a 105 amino acid peptide when a stop codon was introduced in position 106 after the challenge. The NFH-El strain initially had a very short VP5 ORF, only 28 amino acids long, which was maintained after the challenge.