Figure 3.
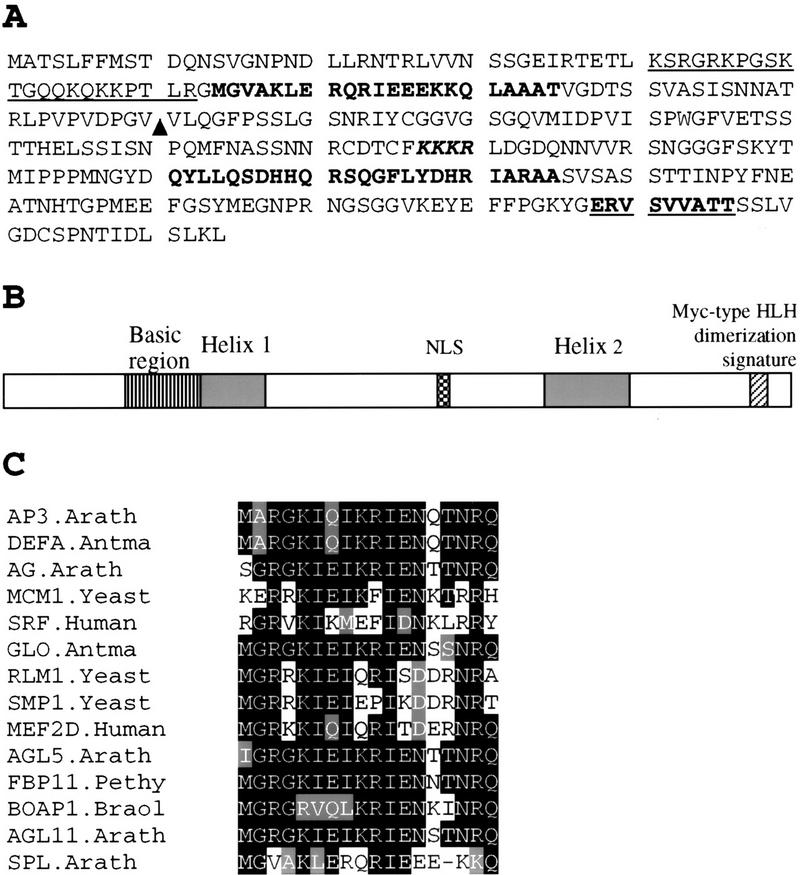
Sequence analysis of SPL polypeptide. (A) Amino acid sequence predicted from the SPL cDNA clone (accession no. AF159255). Underlined sequence from 41 to 62 is a basic region. Sequences in boldface type, 63–85 and 211–235, are putative helix regions. KKKR is a putative nuclear localization signal. Bold underlined sequence, 287–296 represents the putative Myc-type helix–loop–helix dimerization signature. (▴) Ds insertion site in spl. (B) Schematic drawing shows SPL protein domain structures starting with the amino-terminal at left. (NLS) Nuclear localization signal. (C) Comparison of SPL protein region between residues 63 and 85 with the helix 1 of the MADS domain from AP3.Arath (accession no. P35632); DEFA.Antma (accession no. P23706); AG.Arath (accession no. P17839); MCM1.Yeast (accession no. P11746); SRF.Human (accession no. P11831); GLO.Antma (accession no. Q03378); RLM1.Yeast (accession no. Q12224); SMP.Yeast (accession no. P38128); MEF2D.Human (accession no. Q14814); AGL5.Arath (accession no. P29385); FBP11.Pethy (accession no. X81852); BOAP1.Braol (accession no. Z37968); AGL11.Arath (accession no. U20182). Residues identical or similar to the SPL sequence are shaded. The dash indicates a gap.
