Figure 2.
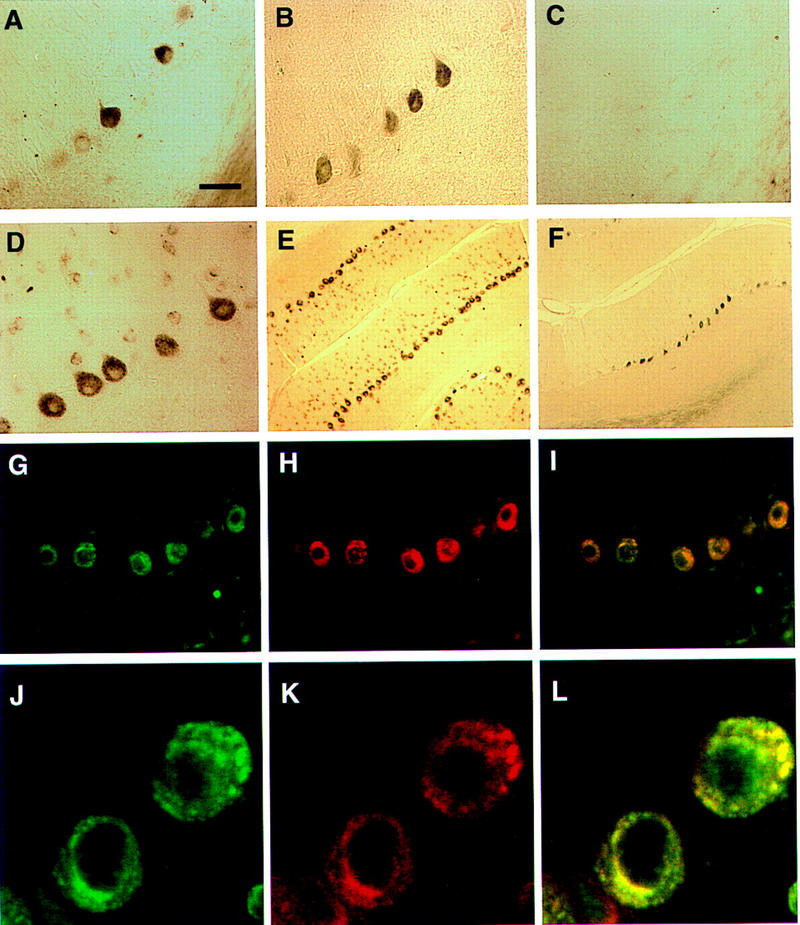
Immunohistochemical colocalization of cdr2 and c-Myc in the cytoplasm of rat cerebellar Purkinje neurons. (A) A section of adult rat cerebellar cortex stained with anti-c-Myc mouse polyclonal antibody N262 shows strong reactivity with some but not all cerebellar Purkinje neurons. (B) Purkinje neuronal reactivity with a different anti-c-Myc antibody, C-19. (C) Reactivity with C-19 after preincubation with immunizing peptide (2 μg/ml). (D) Reactivity with PCD CSF (anti-cdr2) reveals cdr2 immunoreactivity in the cytoplasm of Purkinje cells. (E), Low power view of cerebellum reacted with PCD CSF, reveals that Purkinje neurons are uniformly labeled. (F) A section obtained near (∼24 μm) the section in (E) stained with anti-c-Myc antibody C-19, illustrating isolated groups of c-Myc expressing Purkinje neurons. (G) Immunofluorescent photograph of rat Purkinje neurons reactive with PCD CSF visualized with Cy-2-conjugated anti-human antibody. (H) Same neurons as (G) visualized with anti-c-Myc antibody and with Cy-3-conjugated anti-rabbit antibody. (I) Fusion of images in G and H showing overlap in the expression of both proteins within individual neurons; some neurons in the molecular layer (presumably stellate neurons) stain lightly with cdr2 antibody but not with c-Myc antibody. (J), Confocal laser image of cdr2 expression in a single 2–μm optical section, imaged with Cy-2-conjugated anti-human antibody. (K) Same 2–μm section as J visualized with anti-c-Myc polyclonal C-19 antibody and with Cy-5-conjugated anti-rabbit antibody. (L) Fusion of images in Jand K showing colocalization of both cdr2 and c-Myc within the Purkinje neuronal cytoplasm. (A–D, G–IBar, 20 μm; (E,F) bar, 80 μm; (J–L) bar, 3.4 μm.
