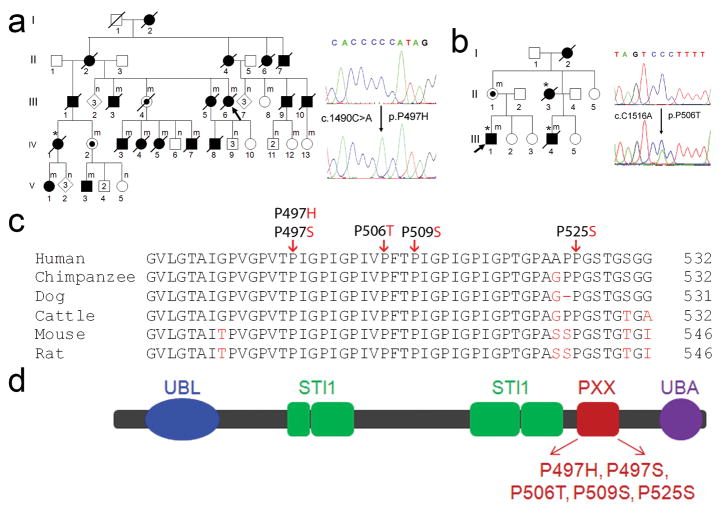
Fig. 1.
Mutations of UBQLN2 in patients with ALS and ALS/dementia. (a) A mutation, c.1490C>A, resulting in p.P497H, was identified in a large family with ALS (F#186). This family was used to map X-chromosome-linked ALS. The pedigree is shown on the left and sequences are shown on the right. The wild-type sequence is shown in the upper panel. A representative hemizygous mutation in a male patient (V3) is shown in the lower panel. All of the affected members whose DNA samples were available for sequencing analysis had the mutation. Two obligate carriers (III4 and IV2) were identified to have the same mutation. For simplicity and clarity, more than one unaffected individual of both genders is represented by a single diamond and more than one unaffected male individual is represented by a single square. Individuals with mutation in the UBQLN2 are labeled by (m) and those without mutation are labeled by (n). (b) A mutation c.1516C>A (p.P506T) was identified in F#6316. Shown in the right lower panel is a heterozygous mutation from a female obligate carrier (II1). (a–b) Probands are indicated with arrows and patients with dementia are indicated with asterisks. (c) Evolutionary conservation of amino acids in the mutated region of ubiquilin2 in different species. Comparison of human (H. sapiens) ubiquilin and its orthologues in chimpanzee (P. troglodytes), dog (C. lupus familiaris), cattle (B. taurus), mouse (M. musculus) and rat (R. norvegicus). Amino acids identical to human UBQLN2 are in black letters and non-identical ones are denoted in red letters. The positions of the C-terminal amino acids are shown on the right. The mutated amino acids are indicated by arrows on the top. (d) Predicted structural and functional domains of ubiquilin2. Ubiquilin2 is a protein of 624 amino acids. Predicted structural and functional domains include a UBL (ubiquitin-like domain, 33–103), four STI1 (heat shock chaperonin-binding motif), a 12 PXX repeats (491–526) and a UBA (ubiquitin-associated domain). ALS- and ALS/dementia-linked mutations are clustered in the 12 PXX repeats.