Figure 6.
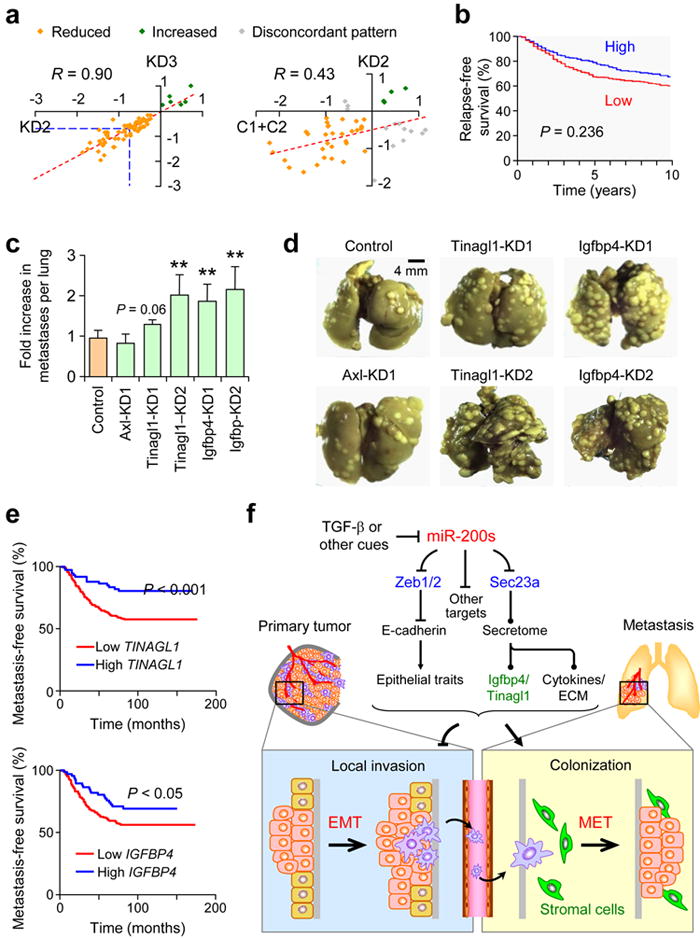
Sec23a knockdown disrupts secretion of proteins that are correlated with suppression of clinical metastasis. (a) Scatter plot showing correlation of secretome profiles between two different Sec23a KD lines and between Sec23a KD and C1+C2 lines. Proteins in common between different lines were used to generate the plots. Orange dots represent proteins reduced in abundance in both conditions; green dots represent proteins increased in abundance in both conditions whereas gray dots represent those proteins that show discordant expression patterns. (b) Kaplan-Meier curves showing relapse-free survival of patients with high and low median expression level of 35 genes reduced in secretion in Sec23a KD lines. (c) Bar graph showing fold increase in number of pulmonary metastases in 4TO7-derived lines stably knocking down Axl, Tinagl1 or Igfbp4 relative to vector control. (d) Representative gross lung images from animals injected via lateral tail vein with various knockdown lines from (c) along with vector control. ** P < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). (e) Kaplan-Meier plots of distant metastasis-free survival of patients in the EMC286 dataset stratified by expression of TINAGL1 (top) or IGFBP4 (bottom). P values were computed by log-rank test. (f) Schematic model of miR-200 function during metastasis. MiR-200s simultaneously target several genes including Zeb1, ZEB2 and Sec23a to inhibit local invasion but promote metastatic colonization. Targeting of Zeb1/2 influences cell-intrinsic epithelial traits whereas targeting of Sec23a modulates tumor-derived secretion of factors such as Igfbp4 and Tinagl1, which influence metastatic colonization by altering tumor-stromal interactions.
