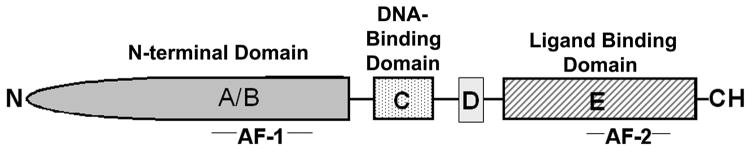
Figure 1.
Domain structure of the androgen receptor. The androgen receptor is composed of a N-terminal domain (NTD) or A/B domain, with transactivation function mediated through the AF-1 region, a DNA-binding (DBD) or C domain, harboring two zinc finders that recognize AREs in regulated genes, a hinge region or D domain, and a ligand-binding (LBD) or E domain that contains the steroid binding pocket and helices 11 and 12 as well as the activation function-2 region (AF-2).