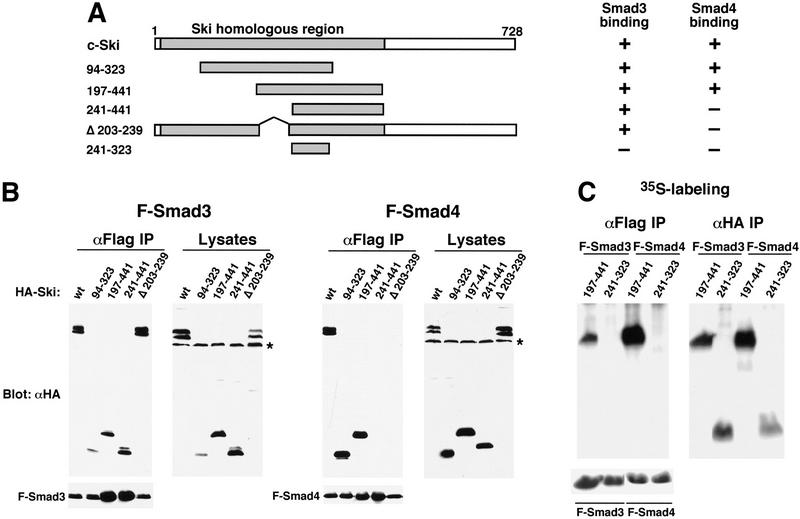
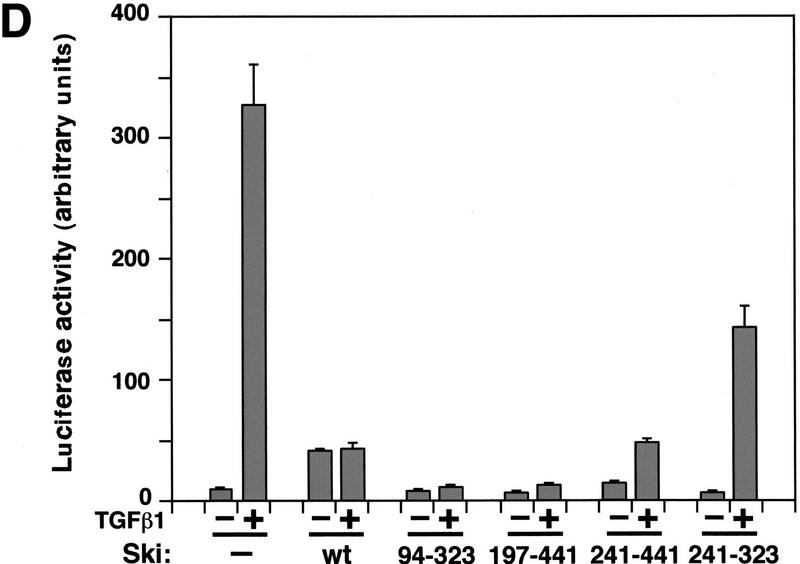
Figure 5.
Smad proteins interact with the amino-terminal region of Ski. (A) Schematic drawings of Ski truncation mutants. The domain in c-Ski that is conserved with v-Ski (residues 24–441) is shaded. This domain contains transforming activity and also mediates binding to N-CoR. (B) Binding of the Ski mutants to Smad3 and Smad4. Flag–Smad3 or Flag–Smad4 were cotransfected with HA-tagged c-Ski and mutants. Association of Smads with various Ski proteins was analyzed by blotting of the Flag immunoprecipitates with an anti-HA antiserum. Cell lysates were blotted directly with an anti-HA antibody as a control for the expression of various Ski mutants. (*) A nonspecific background band. (C) Interaction of Smad3 and Smad4 with Ski(241–323). To detect the smallest Ski truncation mutant, 293T cells transfected with Flag–Smads and HA–Ski(214–323) were labeled with 35S-Express, and Smad-bound Ski(241–323) was isolated by immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag agarose and visualized by autoradiography. Parallel immunoprecipitation with an anti-HA antiserum was carried out to control for the expression of the Ski mutants. Ski(197–441) was used as a positive control for this experiment. (D) Hep3B cells were transfected with p3TP–lux and various Ski mutants. After transfection (30 hr), cells were stimulated with 50 pm TGFβ1 for 16 hr and luciferase activity was measured.