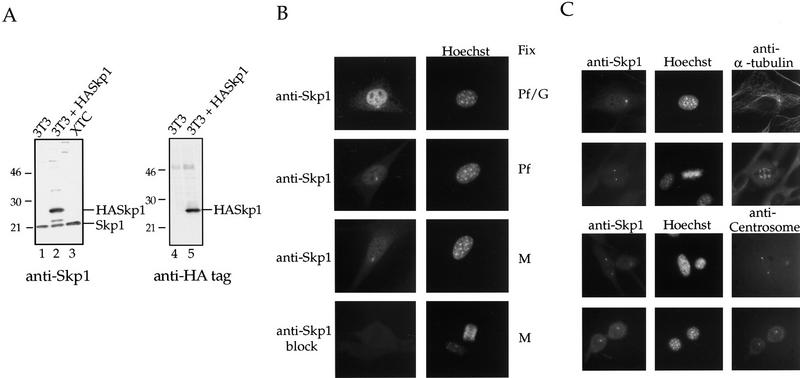
Figure 1.
Characterization of Skp1 antibodies and localization of Skp1 in cells. (A) Western blotting using affinity-purified anti-Skp1 antibodies. (Lanes 1,4) NIH-3T3 cell lysate; (lanes 2,5) lysate of NIH-3T3 cells transiently transfected with HA-tagged Skp1; (lane 3) XTC cell lysate. The blots were incubated with affinity-purified anti-Skp1 antibodies (lanes 1–3) or with rabbit anti-HA antibodies (lanes 4,5), followed by secondary antibodies, and bands visualized using enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) Western blotting detection reagents. Positions of molecular weight markers are indicated. (B) Immunofluorescence localization of Skp1. Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde (Pf), a paraformaldehyde/glutaraldehyde (Pf/G) mixture, or methanol (M) as indicated, and labeled with affinity-purified anti-Skp1 antibodies (top three panels) or anti-Skp1 antibodies blocked with excess GST–Skp1 protein (bottom panel) and with Hoechst dye to label DNA. (C) Costaining confirms centrosomal localization. NIH-3T3 cells were fixed in methanol and stained with affinity-purified anti-Skp1 antibodies and either mAb against α-tubulin or human anti-centrosome antiserum as indicated, followed by secondary antibodies and Hoechst dye.