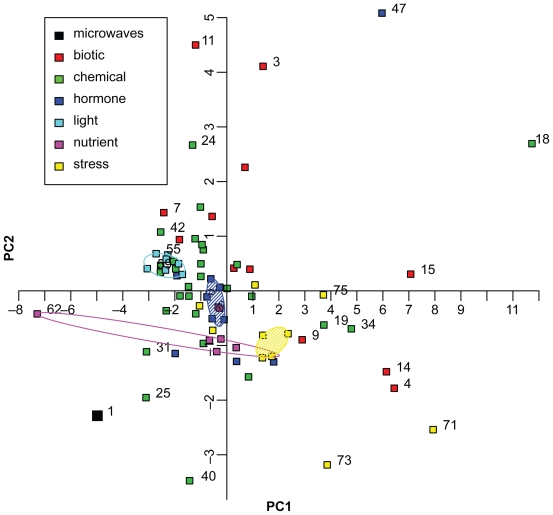
Figure 3.
Principal Component Analysis of 75 ATH1 microarray datasets. The fold changes of 10 genes differentially expressed in the microwave dataset (Table 2, no. 1 in Figure 3) were compared with fold changes of 74 ATH1 microarray datasets of Genevestigator (no. 2 to 75). The categories based on several datasets are: “biotic”, “chemical”, “hormone”, “light”, “nutrient”, and “stress” conditions, and are shown by symbols as indicated in the graph. Convex hulls encircle datasets treated with different light conditions (turquoise) or nutrient availability (magenta). Datasets treated with phytohormones (blue) or stress conditions (yellow) are encircled by a robust convex hull, disregarding data points on the outer convex hull and encompassing the remaining data points. The following datasets are displayed but not all of them are numbered in the graphic: 1. microwaves, 2. A. brassiciola, 3. A. tumefaciens, 4. B. cinerea, 5. E. cichoracearum, 6. E. orontii, 7. F. occidentalis, 8. M. persicae, 9. M. persicae, 10. mycorrhiza, 11. nematode, 12. P. infestans, 13. P. rapae, 14. P. syringae, 15. P. syringae, 16. 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzamide, 17. 4-thiazolidinone/acetic acid, 18. 6-benzyl adenine, 19. AgNO3, 20. aminoethoxyvinylglycine (AVG), 21. brassinazole 220, 22. brassinazole 91, 23. chitin, 24. high CO2, 25. cycloheximide, 26. daminozide, 27. furyl acrylate ester, 28. hydrogen peroxide, 29. ibuprofen, 30. isoxaben, carbobenzoxyl-leucinyl-leucinyl-leucinal (MG13), 31. norflurazon, 33. naphthylphthalamic acid (NPA), 34. ozone, 35. paclobutrazole, 36. p-chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid (PCIB), 37. n-octyl-3- nitro-2,4,6-trihydroxybenzamide (PNO8), 38. prohexadione, 39. propiconazole, 40. syringolin, 41. 2,3,5-triiodobenzoic acid (TIBA), 42. uniconazole, 43. zearalenone, 44. absisic acid, 45. 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC), 46. brassinolide, 47. brassinolide/H3BO3, 48. ethylene, 49. giberellic acid (GA3), 50. indole acitic acid, 51. methyl-jasmonate, 52. salicylic acid, 53. zeatin, 54. white light, 55. blue light, 56. far red light, 57. red light, 58. UV-A-irradiation, 59. UV-AB-irradiation, 60. white light, 61. Cs+, 62. glucose/sucrose, 63. (−) potassium, 64. (−) nitrogen, 65. (−) sulfur, 66. cold, 67. drought, 68. genotoxic, 69. heat, 70. hypoxia, 71. osmotic, 72. oxidative, 73. salt, 74. UV-B, 75. wounding.