Figure 2.
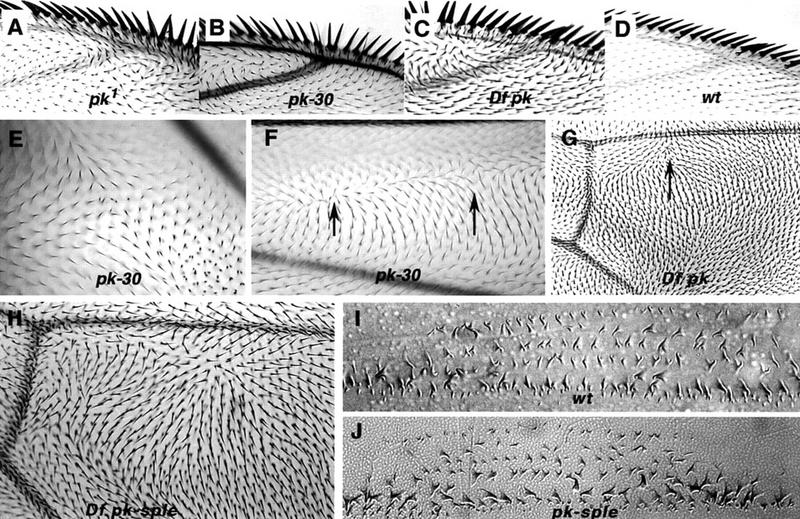
Comparison of wing polarity patterns between different alleles of pkpk. Junction of vein 1 and 2 at anterior margin in pkpk1 (A), Df(2R)pk-30 (B), Df(2R)nap-2/Df(2R)sple-J2 (C), and wild type (D). In pkpk mutant wings, the whorl close to the junction of vein 2 with the wing margin marks a discontinuity in polarity, or stacking flaw. Stacking flaws with different topologies are found in different regions of the wing. (E) Df(2R)pk-30, a cruciform discontinuity posterior to vein 5; note doubled hairs. (F) Df(2R)pk-30, radial and cruciform discontinuities (arrows) between veins 2 and 3. (G) Overlapping pkpk deletions, Df(2R)nap-2/Df(2R)sple-J2. Note triangular dislocation in polarity (arrow) distal to the posterior cross vein as in pkpk1 (Fig. 1A). (H) Overlapping pkpk–sple deletions removing the entire gene Df(2R)pk-N5/Df(2R)sple-J2 (cf. the pkpk–sple13 pattern; Fig. 1B). Embryonic denticle belt in wild type (I) and pkpk–sple13 (J). There is no detectable embryonic phenotype with alleles of pkpk, pksple, or pkpk–sple; in particular, the denticle belt morphology and denticle orientation remains normal.
