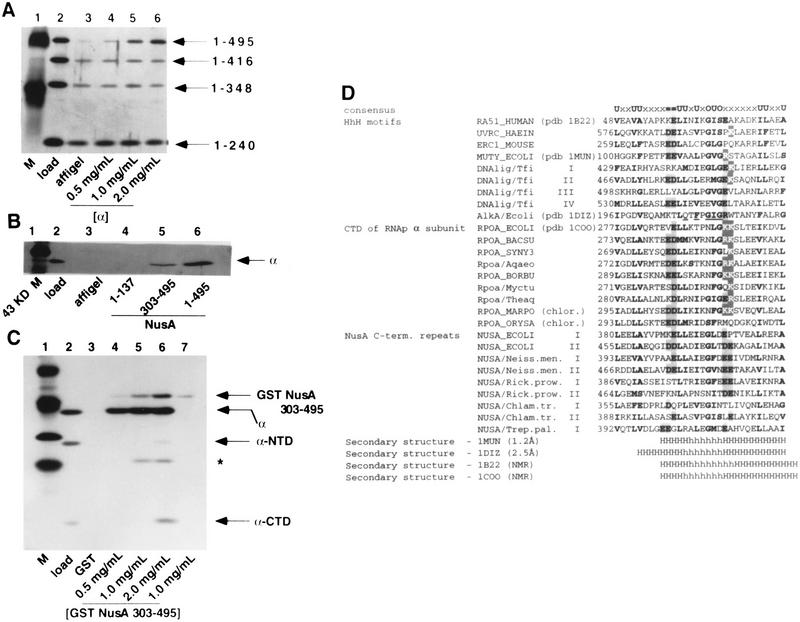
Figure 3.
Interaction of α with the carboxy-terminal region of NusA. (A) Carboxy-terminal truncation of NusA prevents the α–NusA interaction. A mixture of four His6-tagged NusA proteins (lane 2) was passed over columns containing affigel (lane 3) or increasing amounts of affigel-coupled α (lanes 4–6). Bound proteins were eluted with buffer containing 1M NaCl, subjected to SDS-PAGE, and stained with silver. (B) The carboxy-terminal region of NusA interacts directly with α. Buffer containing α and 0.2 mg/ml insulin (lane 2) was passed over columns containing affigel (lane 3) or affigel-coupled NusA (2 mg/ml) (lane 6) or affigel-coupled regions of NusA (lanes 4 and 5) (as indicated). The concentrations of amino- and carboxy-terminal regions of NusA on the columns were adjusted so that each had the same molar concentration as the full-length NusA. Bound protein was eluted with buffer containing 1 M NaCl, subjected to SDS-PAGE, and stained with silver. (C) α-CTD interacts with the 192 carboxy-terminal amino acids of NusA. A mixture of α, α-CTD, and α-NTD (lane 2) was passed over columns containing GST (lane 3) or increasing amounts of GST–NusA (amino acids 303–495) (lanes 4–6). As a control, buffer alone was passed over a GST–NusA (amino acids 303–495) column (lane 7). Bound proteins were eluted with buffer containing 1 M NaCl, subjected to SDS-PAGE, and stained with silver. * indicates a degradation product of α, as identified by mass spectrometry. (D) Helix–hairpin–helix motifs in the carboxy-terminal domains of bacterial RNA polymerase α subunits and NusA proteins. Identifiers in SWISSPROT and PDB databases are shown where available. Numbers indicate the distance, in amino acid residues, from the amino terminus of the protein. Roman numerals indicate the repeated motifs in the same protein. Residues conserved in many families of HhH proteins are indicated by bold type. Within the consensus line, certain categories are indicated: bulky hydrophobic residues (F, I, L, M, V, W, and Y; U in the consensus line), small side chains (A, G, and S; O in the consensus line), negatively charged residues (D and E; = in the consensus line), and positively charged residues (K and R; outlined letters in the alignment). Residues that may participate in charge–charge interactions are boxed. Underlined letters in the E. coli AlkA mismatch repair glycosylase sequence indicate the amino acids whose side chains make contacts with the phosphate residues in the DNA backbone, either directly or by coordinating a metal ion. The known elements of secondary structure are indicated by H for helix and h for hairpin.