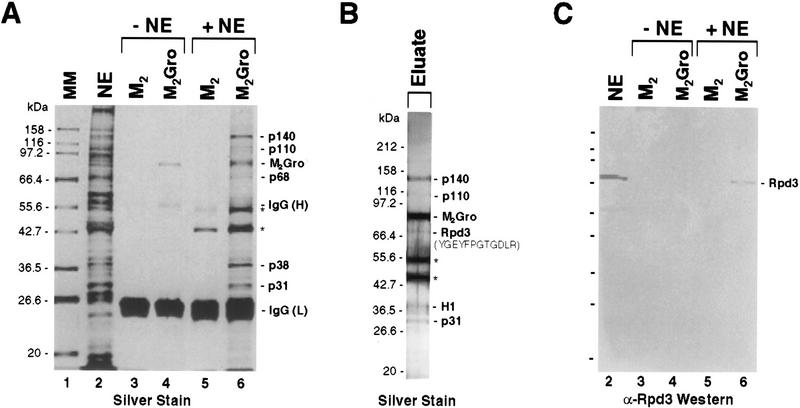
Figure 1.
Affinity purification of Gro-interacting proteins. (A) Silver-stained SDS–polyacrylamide gel showing results of a small scale affinity purification of Gro-interacting proteins. (Lane 1) Molecular mass markers; (lane 2) unfractionated 0- to 12-hr Drosophila embryonic nuclear extract; (lanes 3–6) SDS elutions of M2 antibody beads lacking (M2, lanes 3,5) or containing (M2Gro, lanes 4,6) epitope-tagged Gro. (Lanes 5,6) The beads were incubated with embryonic nuclear extract and subsequently subjected to extensive washing prior to SDS elution; (lanes 3,4) the nuclear extract was omitted. IgG light (L) and heavy (H) chains are indicated. Polypeptides from the embryonic nuclear extracts that uniquely coprecipitate with the M2Gro beads are indicated (p140, p110, p68, p38, and p31). (*) Two polypeptides that are retained on the beads in both the presence and absence of Gro. (B) Silver-stained SDS–polyacrylamide gel showing an aliquot of the eluate from a large-scale M2Gro affinity column used for affinity purification of Gro-interacting proteins. Elution was achieved by washing the beads with excess Flag peptide. Thus, unlike in A, the immunoglobulin chains were not eluted. However, the same two nonspecific polypeptides (*) that eluted with SDS (A), eluted with the peptide, indicating that they are probably binding directly to the antibody. The amino acid sequence denotes a peptide sequence obtained from an internal lysC fragment of p68. This sequence is a perfect match to a predicted lysC fragment in Drosophila histone deacetylase, Rpd3. P38 has been identified as Drosophila histone H1 (H1). (C) Immunblot with anti-Rpd3 antibody. Lanes are the same as in A.