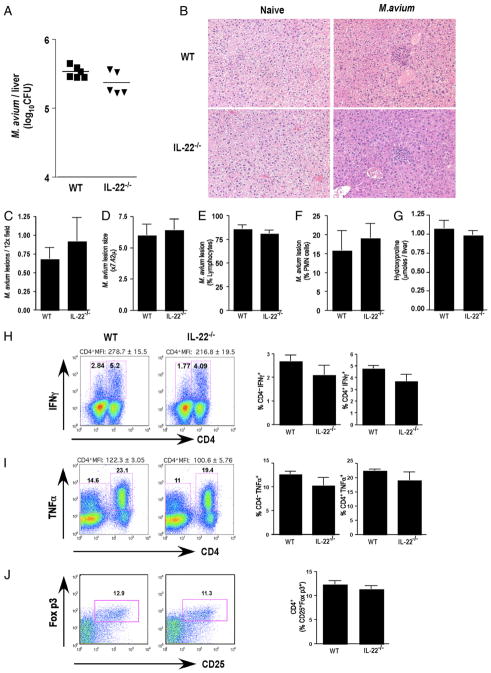
FIGURE 3.
Efficient control of M. avium despite IL-22 deficiency. Mice were i.v. infected with 5 × 106 CFU of M. avium (Strain SmT 2151). Bacterial loads in infected mice were determined at day 30 postinfection. One of two experiments with five mice per group showing mean ± SEM (C–G, H–J) or individual mice per data point are shown (A). A, M. avium CFU in the liver following 30 d of infection. B, Paraffin-embedded liver sections stained with H&E (×10 magnification). C, M. avium lesion frequency in the liver following 30 d of infection. D, M. avium lesion size in the liver following 30 d of infection. E, Percentage of lymphocytes in M. avium lesions. F, Percentage of polymorphonuclear neutrophils in M. avium lesions. G, Hydroxyproline content, as an indicator of hepatic fibrosis, in M. avium-infected liver following 30 d of infection. H, Frequency of IFN-γ+ lymphocytes in spleen. I, Frequency of TNF-α+ lymphocytes in spleen. J, Frequency of CD25+Foxp3+ in CD4+ cells in spleen.