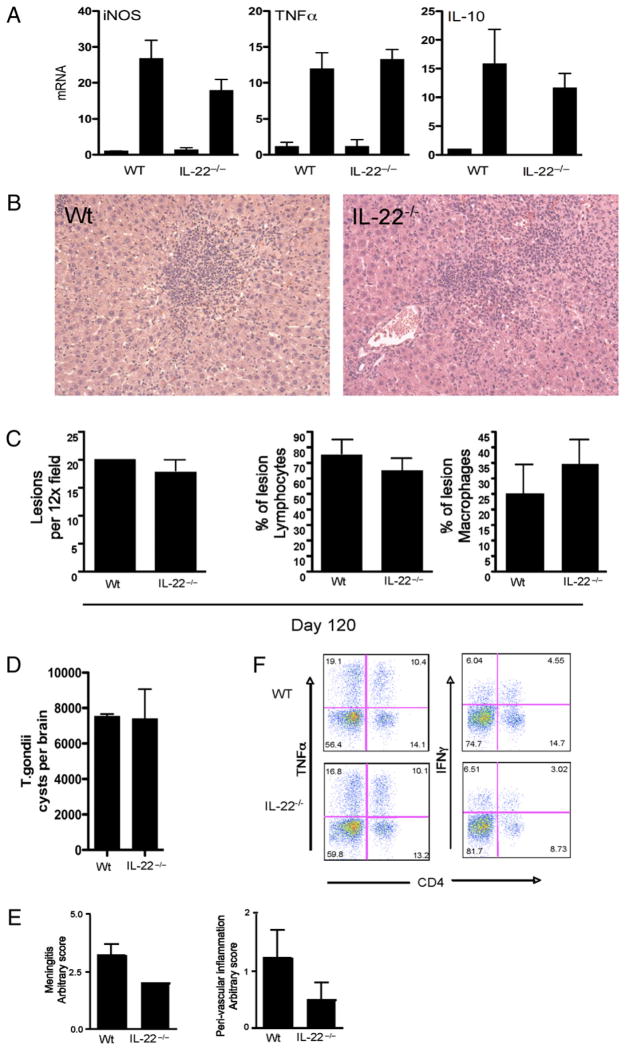
FIGURE 6.
T. gondii -associated liver pathology and control of chronic infection are not altered inil22−/− mice. Micewere infected with T. gondii (ME49 strain) as in Fig. 5. One of two experiments, with five mice per group, is shown. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (A, C–E). A, Expression of iNOS, TNF-α, and IL-10 mRNA in liver of 30-d T. gondii-infected mice. B, H&E-stained liver section taken from WT and il22−/− mice infected for 30 d (×20 magnification). C, Liver lesion frequency, percentage of lymphocytes, and percentage of macrophages. D, T. gondii cyst frequency in brain tissue infected for 120 d. E, Brain pathology with meningitis and peri-vascular inflammation score. F, Brain-infiltrating lymphocytes stained for CD4, TNF-α, and IFN-γ.