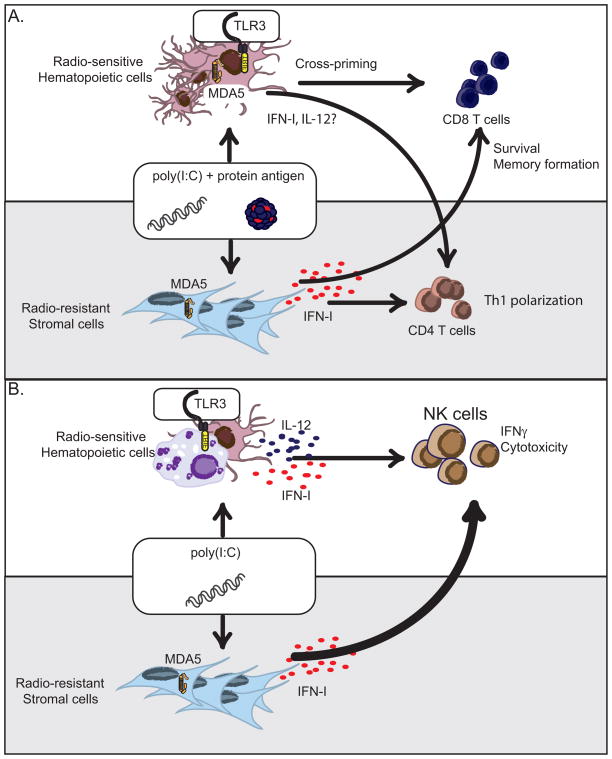
Fig. 2. Hematopoietic and stromal contributions to poly(I:C)-mediated immunity.
(A). Poly(I:C) promotes CD4+ and CD8+ T cell immunity through the production of IFN-I and other cytokines. Poly(I:C)-mediated IFN-I responses are dependent on stromal expression of MDA5. However, adjuvant effects of poly(I:C) on CD4+ T cell immunity require MDA5 expression in both hematopoietic and stromal compartments. Poly(I:C) triggers the TLR3 pathway in CD8α+ DCs to promote cross-presentation to CD8+ T cells while signaling through MDA5 pathway in stromal cells promotes CD8+ T cell survival and memory formation. (B). Poly(I:C) promotes NK cell activation through the production of IFN-I and IL-12. NK cell activation via IFN-I depends on MDA5-expressing radio-resistant stromal cells while TLR3+ hematopoietic cells promote NK cell activation through IL-12 secretion. The MDA5 pathway plays a dominant role in NK cell responses to poly(I:C) while the TLR3 pathway has a secondary effect.