Figure 2.
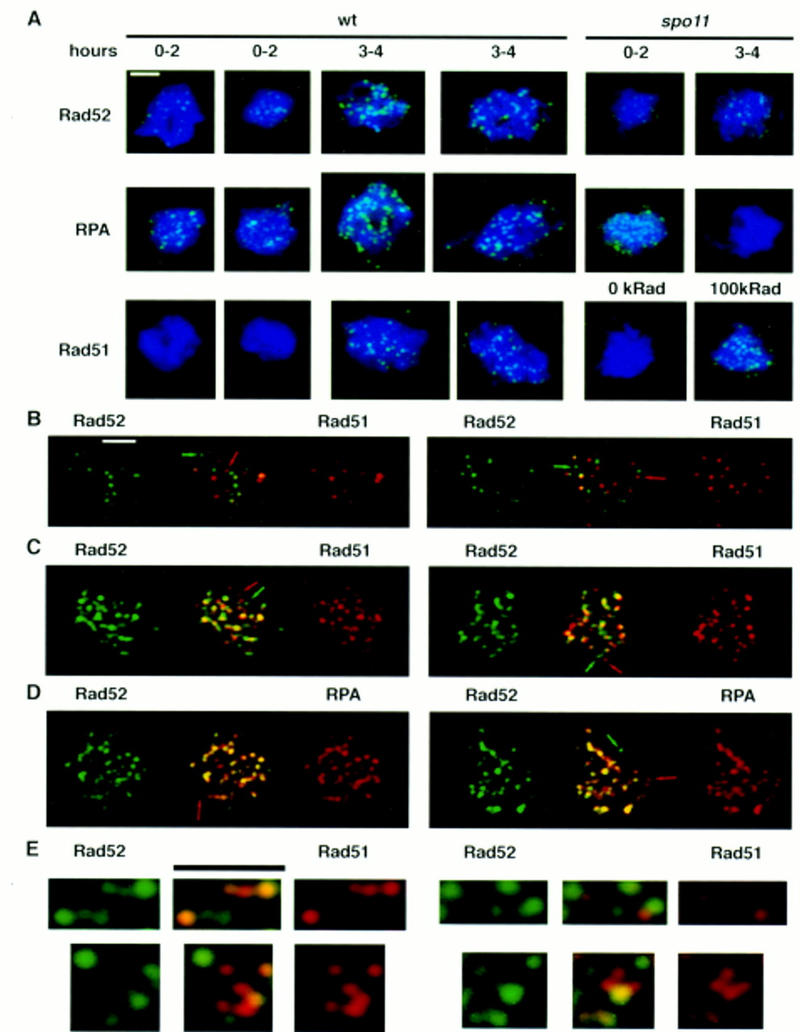
Rad52, RPA, and Rad51 localize to discrete complexes in spread meiotic nuclei. Cells were induced to undergo sporulation and spread meiotic nuclei were prepared and immunostained with antibodies that bind Rad52, RPA, or Rad51, (see Materials and Methods). All nuclei were stained with DAPI to detect chromatin. Pictures shown are pseudocolored composites of monochrome images. Immunostaining patterns are shown in green and DAPI staining patterns in blue. (A) Anti-Rad52, anti-RPA, and anti-Rad51 immunostaining of wild-type and spo11 meiotic nuclei. Nuclei shown are typical of those seen at the times indicated. In the Rad51-staining set one of the spo11 mutant nuclei shown was treated with a dose of 100 krads of ionizing radiation 1 hr before harvesting (cells were irradiated at 3 hr after meiotic induction). (B,C) Colocalization of Rad52 with Rad51. Double immunostaining with a combination of Rad52 and Rad51 antibodies in wild type (B, 3 hr) and dmc1 (C, 7 hr). Antibodies used were rabbit anti-Rad52 and guinea pig anti-Rad51. Single-staining images are pseudocolored from the original black and white images and the merged image is a two-channel combination of the original black and white images. Yellow indicates combination of the two signals. Arrows indicate single-staining foci. (D) Rat anti-Rad52 and rabbit anti-RPA were used for detection in dmc1. The nuclei shown are from the same preparations as in C. (E) Close ups of Rad52–Rad51 double-stained nuclei (using directly conjugated antibodies) showing single-staining foci and double-staining foci with different relative contributions of Rad52- and Rad51-specific signals. Bars, 2 μm.
