Figure 6.
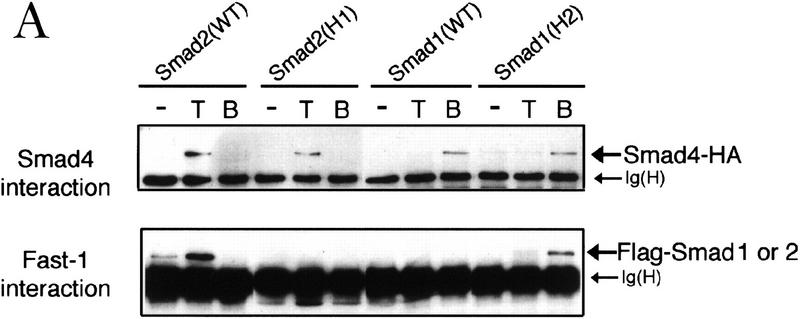
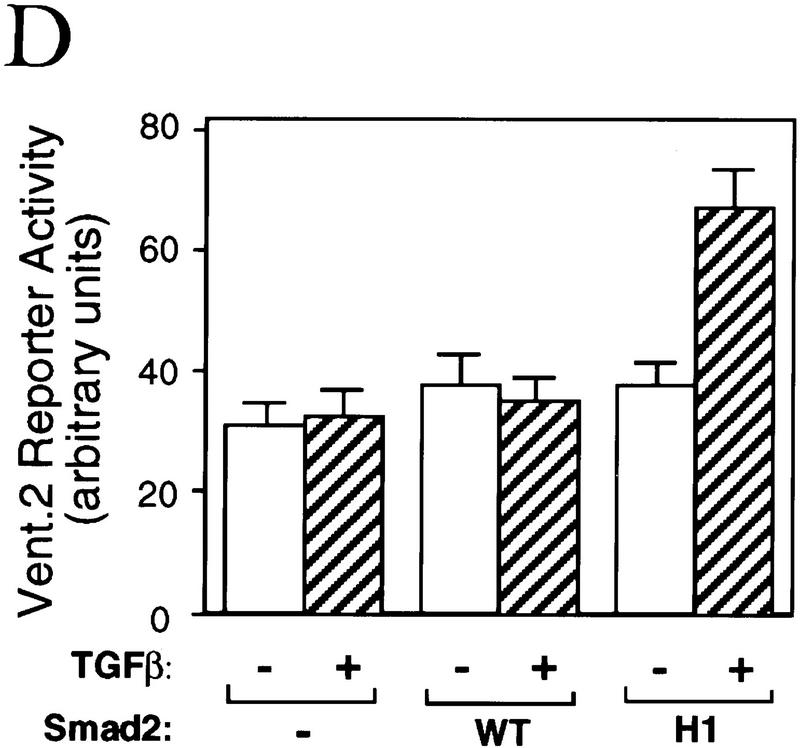
The α-helix 2 of Smad2 specifies the interaction with the DNA-binding factor Fast1. (A) Interaction of wild-type R-Smads and helix 2 exchange mutants with Smad4 and Fast1. HA-tagged Smad4 or myc-tagged Fast1 constructs were cotransfected into COS1 cells with the indicated Flag-tagged forms of Smad1 or Smad2. Transfectants were incubated with TGF-β (T) or BMP2 (B) and the associations of R-Smads with Smad4 (top) and with Fast1 (bottom) were determined. The helix 2 exchange mutants bound Smad4 in response to their agonists, but Smad2(H1) lost the ability to associate with Fast1 whereas Smad1(H2) gained the ability to bind Fast1 in response to BMP. (B) Activation of a Mix.2 reporter by wild-type R-Smads and helix 2 exchange mutants. L17 cells were cotransfected with the indicated forms of Smad1 or Smad2, Fast1, the A3-luciferase construct, and TGF-β receptors or BMP receptors. Cells were incubated with the corresponding receptor ligands, and luciferase activity was determined. Smad2(H1) lost the ability to activate the reporter, whereas Smad1(H2) gained the ability to do so in response to BMP. (C) Fast1-dependent activation of a GAL4 reporter by Smad1(H2). L17 cells were cotransfected with the indicated forms of Smad1, a Fast1 fusion with the DNA-binding domain from yeast GAL4, a GAL luciferase reporter, and BMP receptors. Cells were incubated with or without BMP2, and luciferase activity was determined. (D) Activation of the Vent.2–luciferase reporter in P19 cells cotransfected with TβR-I, TβR-II, and the indicated Smad2 constructs. Cells were incubated with or without TGF-β, and luciferase activity was determined in triplicate samples.