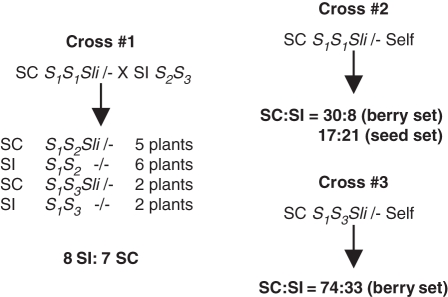
Fig. 1.
Genetic behaviour of S-locus inhibitor (Sli) from Solanum chacoense. Cross #1, a cross between the inbred S. chacoense S1S1 Sli source plant and an SI S. phureja plant designated S2S3. The S. chacoense parent is heterozygous for Sli and behaves as a dominant factor that inhibits SI in half the progeny. SC is unlikely to be due to a defective S-locus since half the progeny are SI. Crosses #2 and #3, selfing the S. chacoense parent or one of the SC progeny of cross #1 also results in SI progeny. Thus, functional S-haplotypes are transmitted through the pollen even when Sli is not.