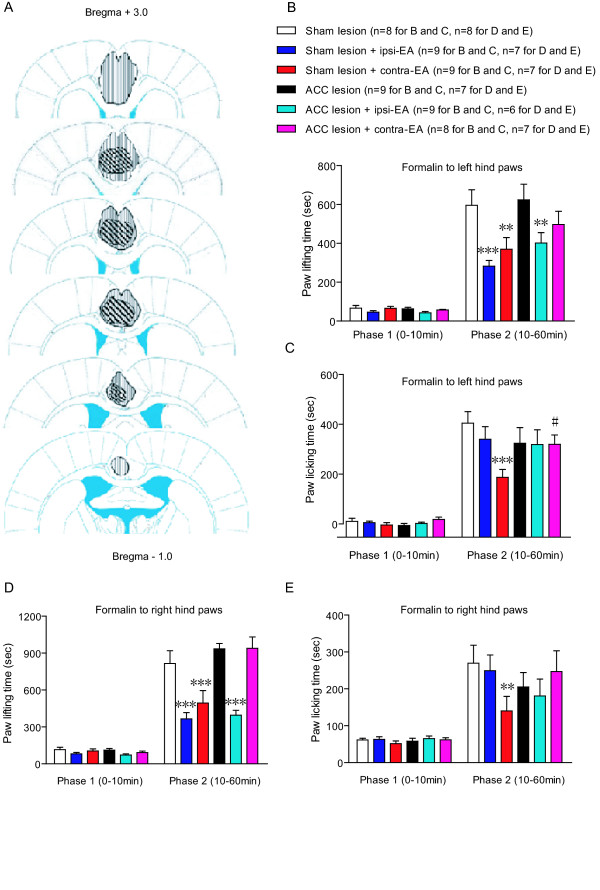
Figure 3.
Effects of rostral ACC lesions on ipsilateral or contralateral EA in the formalin model. A, Schematic representation of the maximum (longitudinal line) and minimum (diagonal line) extent of bilateral ACC lesions. B and D, With formalin injected to the left (B) or right (D) hind paws, rostral ACC lesions reversed the decrease of paw lifting time by contralateral EA, but that by ipsilateral EA was still present. C and E, With formalin injected to the left (C) or right (E) paws, bilateral rostral ACC lesions abolished the decrease of paw licking time by contralateral EA. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001, compared with the formalin group of the corresponding lesion type (sham lesion or ACC lesion). # p < 0.05, compared with the formalin + contralateral EA group of sham lesions. All data were presented as means ± SEM.