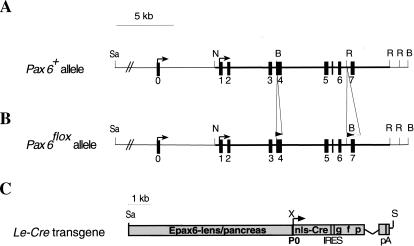
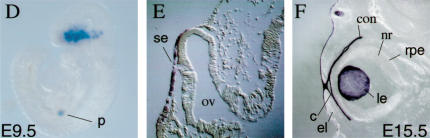
Figure 1.
Targeted insertion of loxP sites into the Pax6 gene and analysis of Cre activity in the Le-Cre transgenic line. Structure of wild-type (A) and targeted (B) Pax6 loci. One loxP site was introduced in exon 4 upstream of the first ATG. The second loxP was followed by the selection cassette flanked by FRT sequences inserted between exons 6 and 7. The selection cassette was removed to establish the Pax6flox allele (see Materials and Methods). (C) Schematic representation of Le-Cre transgene. A 6.5-kb SacII/XmnI genomic region including the upstream regulatory sequences and the first Pax6 promoter (P0) cloned upstream of sequences encoding the nls-Cre followed by internal ribosome binding sites (IRES) and green fluorescent protein (GFP). The recombination pattern was detected by enzymatic reaction (Lobe et al. 1999) on whole mount (D) or sections (E,F) of Z/AP;Le-Cre embryos at E9.5 (D,E) and E15.5 (F). (Arrows) Transcription start sites; (filled rectangles) exons; (open triangle) FRT; (filled triangles) loxP. (c) Cornea; (con) conjuctiva; (el) eyelid; (le) lens; (nls) nuclear localization signal; (nr) neuroretina; (ov) optic vesicle; (p) pancreas; (pA) poly A; (rpe) retinal pigmented epithelium; (se) surface ectoderm. (B) BamHI; (N) NotI; (R) EcoRV; (Sa) SacII; (S) Sfi; (X) XmnI.