Figure 1.
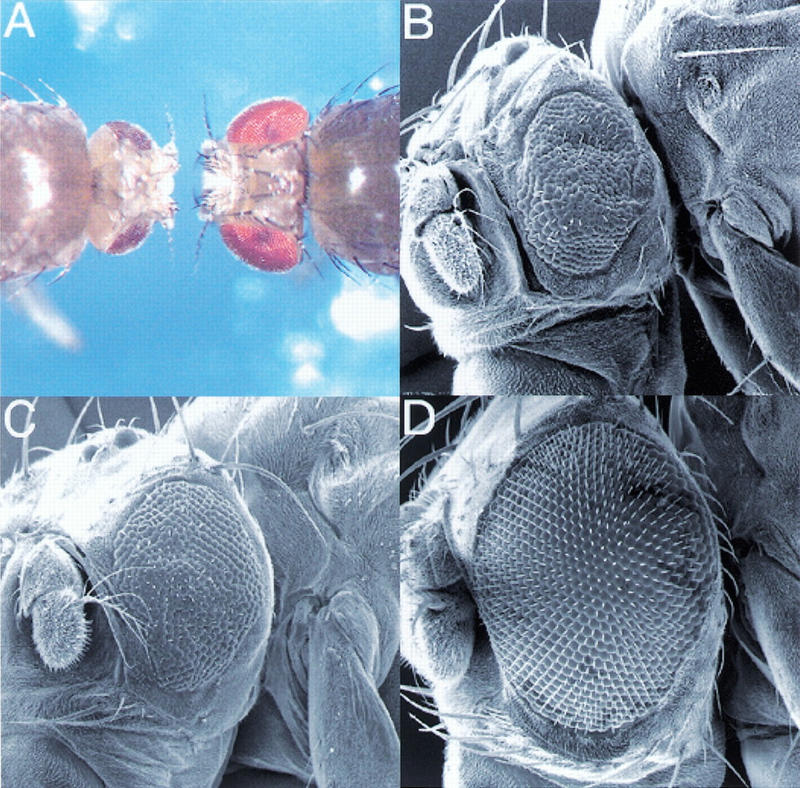
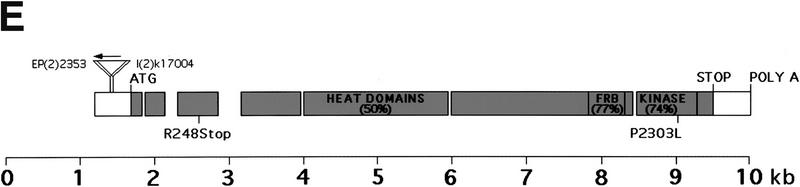
Identification of dTOR. Tissue-specific induction of dTOR2L1 and dTOR2L19 mutant clones using the ey-Flp technique (Newsome et al. 2000) produced flies with reduced head size relative to their body. (A) Dorsal view of y w ey-Flp; P(w+) l(2)2L-3.1 FRT40/CyO y+ (right) and y w ey-Flp; dTOR2L1 FRT40/P(w+) l(2)2L-3.1 FRT40 (left). Flies of the following genotype were examined by SEM: (B) y w ey-Flp; dTOR2L19 FRT40/P(w+) l(2)2L-3.1 FRT40; (C) y w ey-Flp; dTOR2L1 FRT40/P(w+) l(2)2L-3.1 FRT40; (D) wild-type eye. Bar, 100 μm. (E) Genomic structure and mutants of dTOR. The grey region consists of the coding region, and the gaps indicate introns. The percentage amino acid identity of each domain to human TOR is shown in parentheses.