Figure 5.
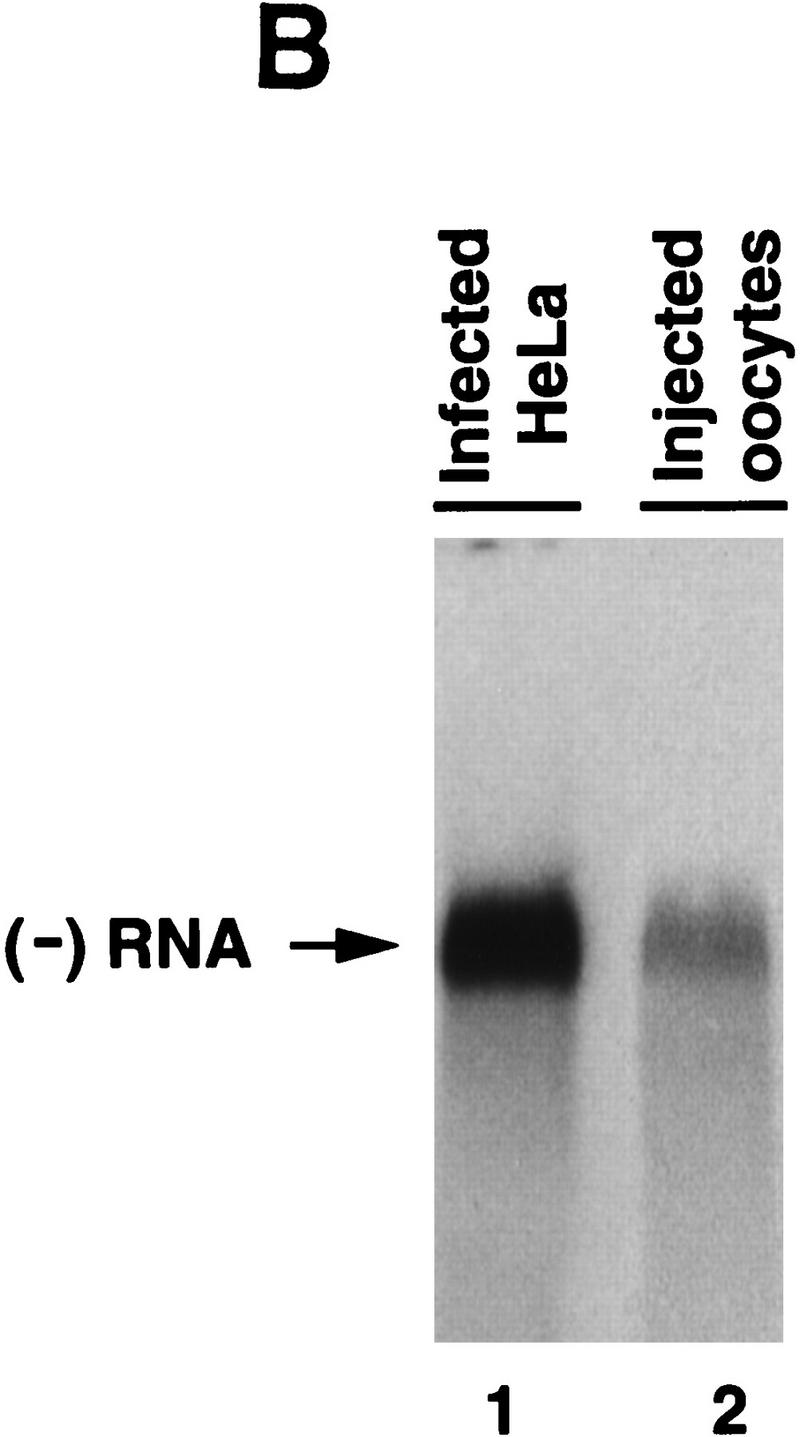
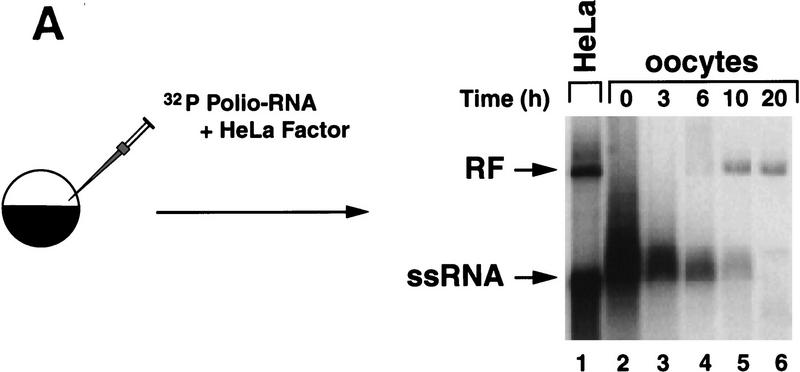
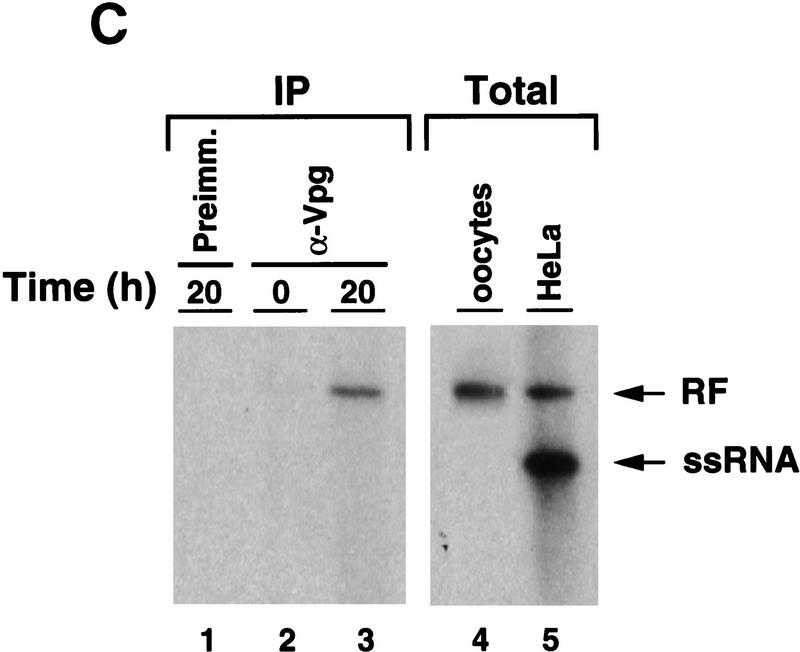
Synthesis of viral negative-strand RNA in Xenopus oocytes. (A) Oocytes were microinjected with in vitro-transcribed 32P-labeled poliovirus RNA together with HeLa S10 extracts (Gamarnik and Andino 1996), and the conversion of the input RNA into a double-stranded form was analyzed as a function of the time in 1% native agarose gels electrophoresis, as indicated on the top. For comparison, 32P-labeled poliovirus RNA was synthesized in crude replication complexes (CRC) obtained from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells (lane 1). Single stranded viral RNA (ssRNA) and the double stranded replicative form (RF), are indicated at left. (B) Northern blot analysis confirms that the oocytes produce negative-strand RNA. Oocyte extracts obtained from 200 oocytes at 20 hr after microinjection of unlabeled viral RNA were used to detect newly synthesized negative-strand RNA (lane 2). DNase- and RNase-treated samples were extracted with phenol–chloroform, ethanol precipitated, and resolved under denaturing conditions through 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. Then, RNA was transferred to a nylon filter, and hybridized with a specific probe complementary to the viral negative strand. As a control, infected HeLa extracts treated in similar conditions was analyzed (lane 1). (C) The replicative form synthesized in oocytes contains a covalently linked Vpg molecule. Oocytes injected with 32P-labeled poliovirus RNA were lysed at 0 and 20 hr post-injection (as described in Materials and Methods), immunoprecipitated with anti-Vpg antibodies (α-Vpg) or preimmune sera (Preimm.), and analyzed in 1% native agarose gel (lanes 1–3). Total RNA from oocytes injected with 32P-labeled poliovirus RNA obtained 20 hr after incubation (lane 4) and 32P-labeled RNA synthesized in crude replication complexes obtained from infected HeLa cells (lanes 5) are shown.