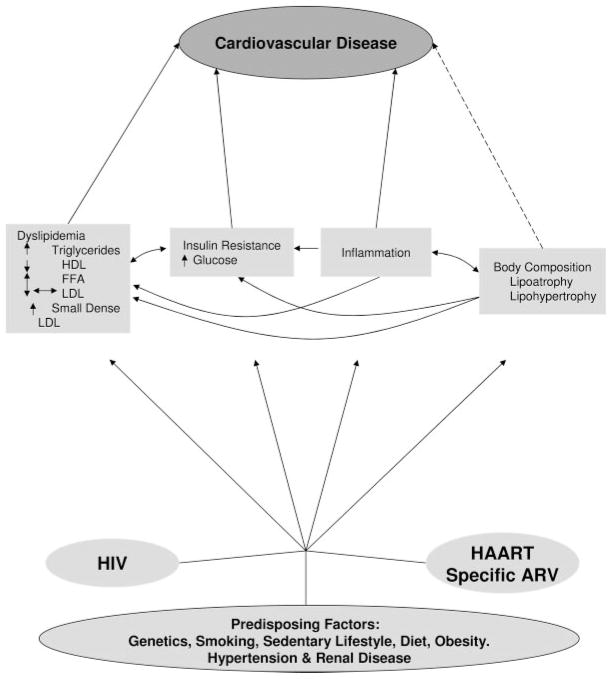
Figure.
Overview of the effects of HIV and its therapies on CVD risk. The contribution of traditional risk factors must be kept in mind, and they may occur with increased prevalence in people with HIV infection (eg, smoking). HIV, likely through the inflammatory response, and antiretroviral therapies independently affect many of the mediators of CVD risk. The effects on lipids are a prominent but complex example; HIV infection lowers LDL levels, but antiretroviral therapy raises LDL back up to normal levels. The bidirectional arrows indicate associations, but there is not yet adequate proof of causality. The dotted arrow between body composition and CVD indicates that body fat is known to affect the mediators such as dyslipidemia and insulin resistance but may also have a direct effect. FFA indicates free fatty acids; ARV, antiretroviral.