Figure 6.
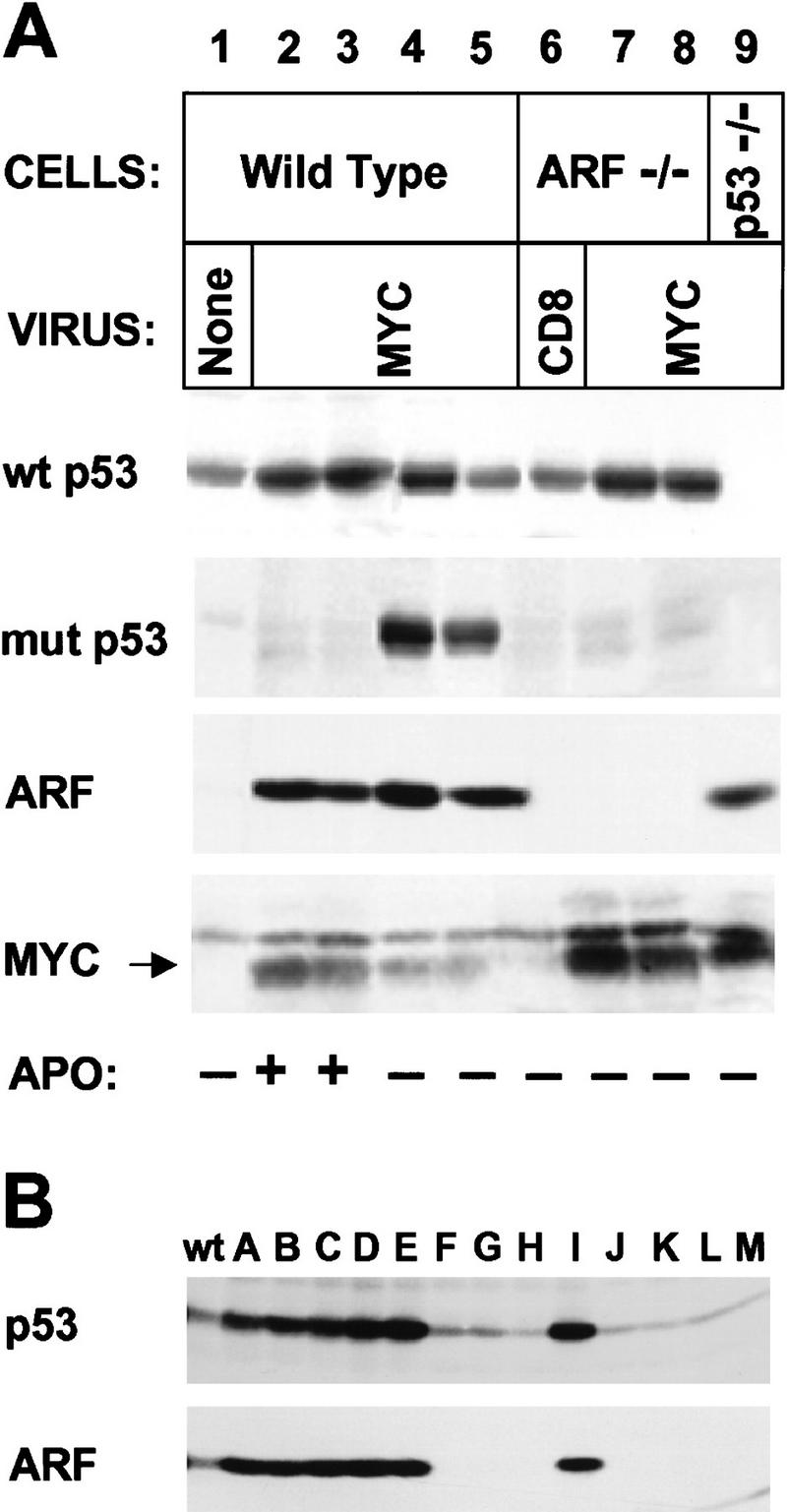
Myc-“immortalized” MEFs lose p53 or ARF function. (A) MEFs of the indicated genotype were infected with CD8 or myc retroviruses at passage 5 after explantation and propagated on a 3T9 protocol. Wild-type cells tested 7–10 days after myc virus infection (lanes 2,3) expressed relatively high levels of p19ARF and wild-type (wt) p53, and were initially sensitive to apoptosis (APO +) when transferred into serum-free medium (see text). However, by 14–21 days postinfection, rapidly growing derivatives were isolated that could grow under serum-free conditions (APO −) and expressed mutant (mut) p53 (lanes 4,5). ARF-null cells infected at passage 5 and transferred 14 days after selection in serum-free medium were resistant to apoptosis but expressed only wild-type p53 (wt) (lanes 7,8). Note that Myc protein levels were significantly higher in ARF-null (lanes 7,8) and p53-null (lane 9) cells than in wild-type MEFs (lanes 2–5). Apoptosis was determined by FACS analysis of propidium iodide- and Hoescht 33342-stained cells. (B) Cells containing a single wild-type ARF allele were infected with myc virus for 4 days and transferred into serum-free medium for 2 days to select for variants resistant to apoptosis. Surviving cells were diluted in microtiter wells and subclones were expanded from single cells in serum-containing medium. Lysates were then blotted for p19ARF and p53. Results with 13 clones (designated A–M) are compared with those obtained with wild-type (wt) uninfected MEFs.
