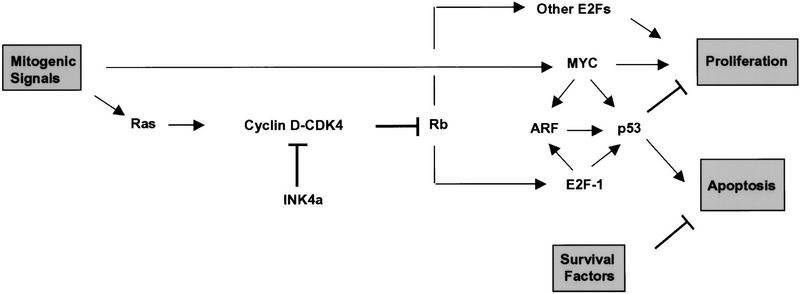
Figure 7.
Model for ARF signaling. ARF is activated via Myc and E2F-1 and acts in turn to trigger p53-dependent cell cycle arrest or apoptosis, depending on the presence of extracellular survival factors. Ras acts through cyclin D-dependent kinases to stimulate pRB phosphorylation, resulting in release of E2F from pRb constraint and activation of E2F-responsive genes. Activation of ARF by MYC and E2F-1 need not be direct, although both transcription factors have been demonstrated to increase ARF mRNA levels (see text). Like Myc, different E2F isoforms are proposed to regulate both cell growth and cell death. In inhibiting cyclin D-dependent kinases, p16INK4a can modulate certain growth-promoting functions of Ras. Other functions of Myc and Ras are not detailed in the schematic.