Figure 2.
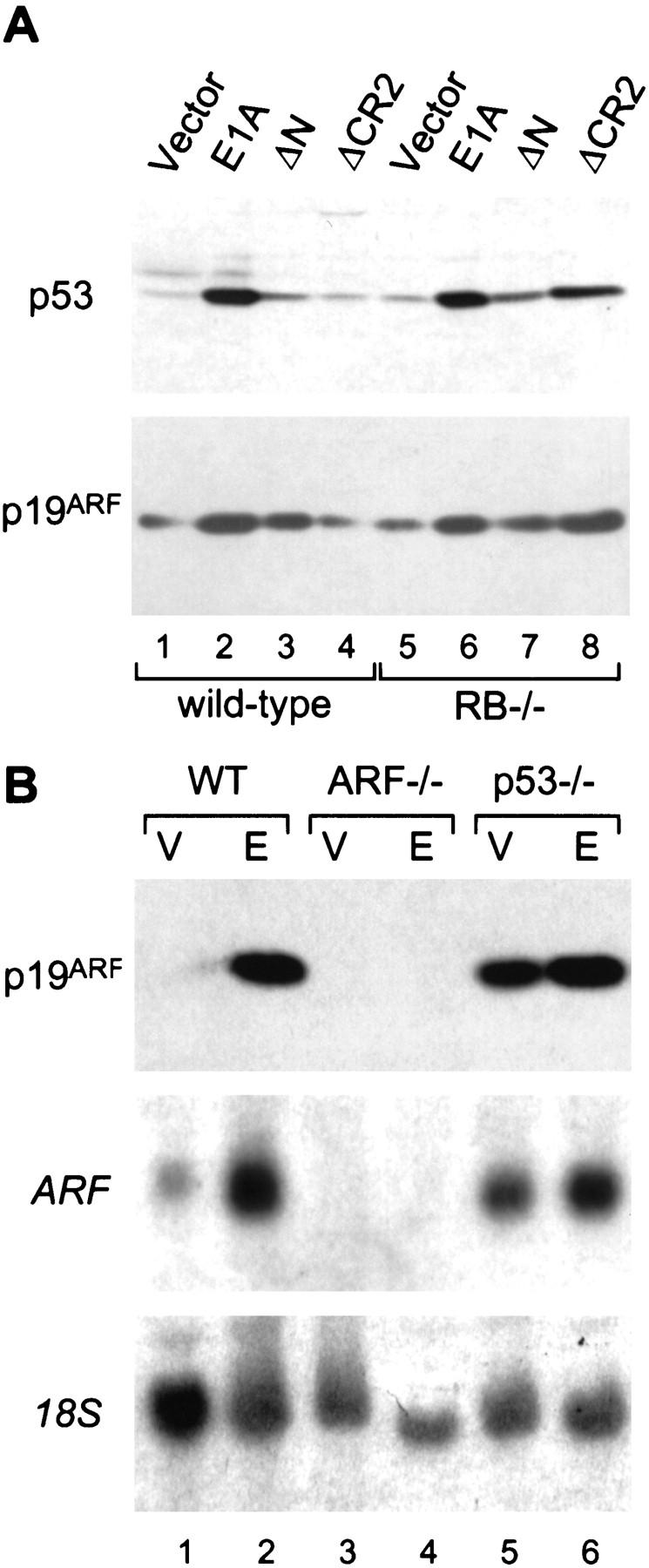
E1A induces p19ARF and p53 through a similar mechanism. (A) Early passage (about three to four) wild-type and Rb−/− MEFs from littermates embryos were infected with retroviruses expressing full-length E1A or E1A mutants unable to bind p300/CBP (ΔN) or the Rb-related proteins (ΔCR2). An empty retroviral vector was used as a control (vector). Immunoblotting was performed using polyclonal antibodies against p19ARF or p53. Using this procedure, each E1A mutant is efficiently expressed at comparable levels (Samuelson et al. 1997). (B) Wild-type (WT), ARF-null (ARF−/−), and p53-null (p53−/−) MEFs were infected with a control vector (V) or a retrovirus expressing full-length E1A (E). Lysates were derived from whole populations passaged minimally in culture (<1 week) and analyzed for ARF protein (top) or mRNA (middle) expression by Western or Northern blotting, respectively. Northern blots were rehybridized using a probe to the 18S rRNA to confirm equal loading (bottom).
