Figure 6.
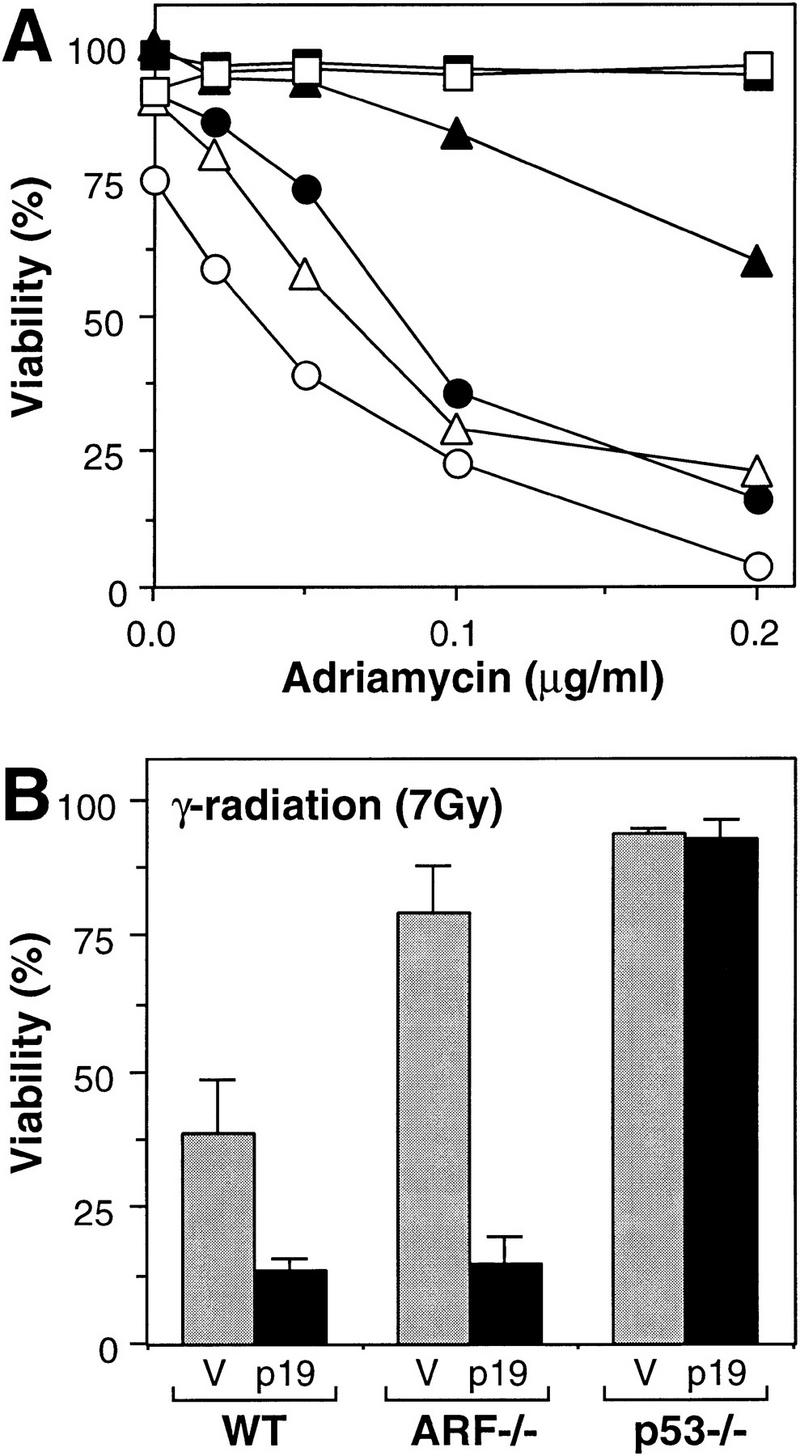
Synergy between p19ARF-dependent and -independent pathways targeting p53. (A) lacZ (solid symbols)- and HA–ARF (open symbols)-expressing cell populations were treated with the indicated doses of adriamycin, and cell viability was determined 24 hr later by trypan blue exclusion. The cell populations were as follows: Wild-type MEFs lacking E1A (squares); wild-type MEFs expressing E1A (circles); ARF−/− MEFs expressing E1A (triangles). Note that ARF−/− and p53−/− MEFs lacking E1A, as well as p53-deficient MEFs expressing E1A, remained viable in adriamycin whether or not they expressed HA–p19ARF (data not shown). (B) lacZ (V, shaded bars) and HA–p19ARF (p19, solid bars) expressing cell populations were treated with 7 Gy ionizing radiation and cell viability was determined 24 hr later by trypan blue exclusion. The values represent the mean and s.d. of at least three separate populations. MEFs not expressing E1A were resistant to apoptosis under these conditions (data not shown; see also Lowe et al. 1993).
