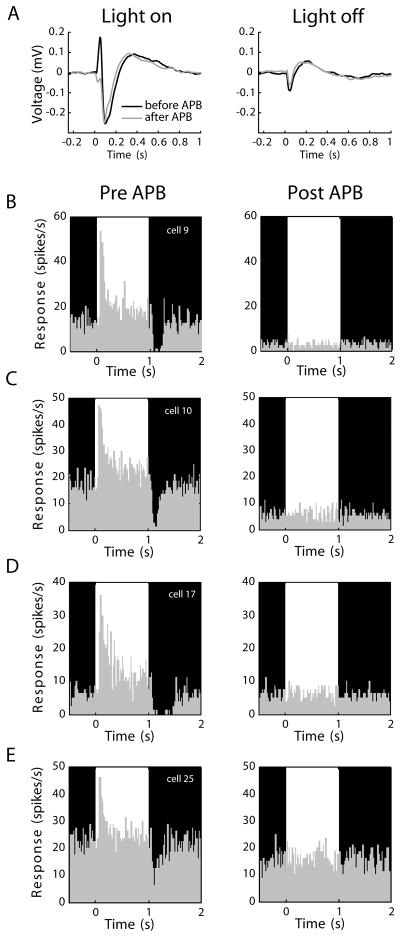
Figure 2.
APB effects in the eye. (A) Electroretinograms (ERGs) showing responses to a repeating full-field stimulus that alternated between a 1-second bright phase and a 1-second dark phase (76 and <1 cd/m2, respectively). Black traces show values before APB, grey traces show values after APB injection. In the light-on condition, the sharp upward deflection before APB injection (black trace) represents the coordinated On-bipolar cell depolarization. This deflection was absent following APB injection (grey trace), confirming APB silenced the On-pathway. In the light-off condition, the ERG was unaffected by APB injection, supporting the view that APB does not cause an enhancement of Off responses in the retina. Axis conventions as in Slaughter and Miller (1981). (B-E) Spiking responses of 4 representative On-center RGCs before and during APB perfusion, in vitro. Recordings were made from excised patches of retina using a 60-channel multielectrode array. In each panel, the bright and dark phases of an alternating stimulus are indicated in the background shading. Each of the On cells shows a clear elevation in spiking activity in response to increases in stimulus luminance. The same cells were unresponsive to visual stimulation during 300 μM APB treatment. Every On-center RGC in our sample (n=32) became visually unresponsive with APB.