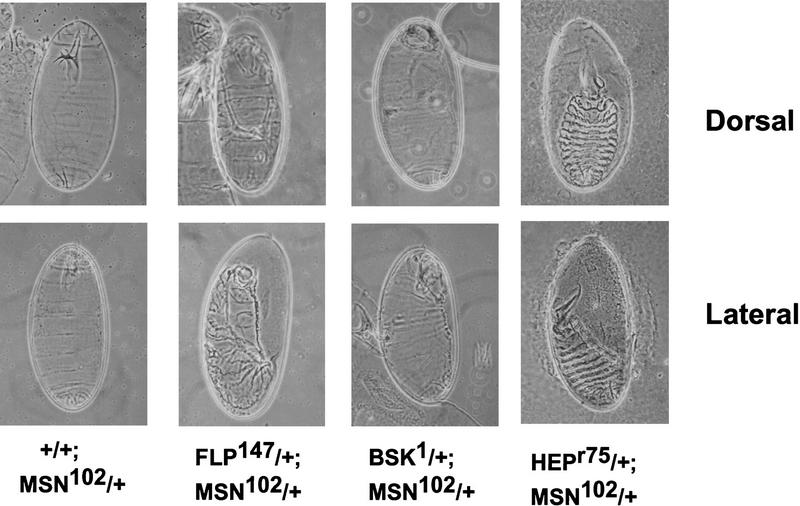
Figure 4.
msn interacts genetically with bsk and hep. Cuticle preparations from embryos obtained from the crosses shown. Crossing msn/+ flies to wild-type flies (+/+) did not lead to a defect in dorsal closure (see Table 1). In contrast to the normal embryos obtained from crossing msn/+ flies with wild-type flies (+/+), crossing msn/+ flies with three different bsk alleles or with hep led to defects in dorsal closure. Note that embryos derived from a cross between Df(2L)flp147/+, which is a complete loss-of-function mutant of bsk, and msn/+ flies display the most severe defect in dorsal closure. (Top) Dorsal views with anterior up; (bottom) lateral views with anterior up.