Figure 2.
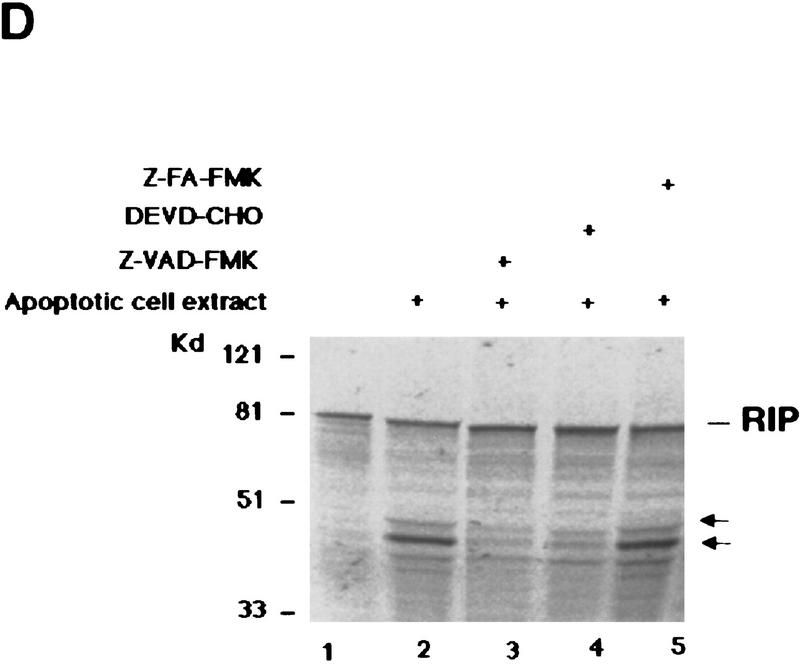
RIP is cleaved by a caspase. (A) HeLa cells were pre-treated with 10 μm of DEVD–CHO (lane 4) or Z–VAD–FMK (lane 3) for 1 hr, or left untreated (lanes 1,2). This was followed by treatment with TNF (15 ng/ml) + CHX (10 μg/ml) (lanes 2–4) for 6 hr. Cell extracts were resolved on SDS-PAGE and Western blotted for RIP (top), PARP (middle), and FADD (bottom). Untreated cells extract was loaded as a control (lane 1). The percentages of dead cells are at the bottom of the panel. (B) 35S-Labeled RIP protein was incubated with apoptotic (lane 3) or normal (lane 2) HeLa cell extracts at 30°C for 3 hr, resolved on SDS-PAGE, and visualized by autoradiography. Nontreated RIP protein was loaded as a control (lane 1). The resultant cleavage products are indicated with arrows. (C) 35S-Labeled Myc-tagged RIP protein was incubated with RIP-depleted apoptotic (lane 6) or normal (lane 5) HeLa cell extracts at 30°C for 3 hr, transferred onto a nitrocellular filter, visualized by autoradiograph, and probed with anti-RIP and anti-Myc to detect the carboxy- and amino-terminal portion of RIP, respectively. Nontreated RIP protein was loaded as a control (lane 4). The resultant cleavage products are indicated with arrows. The normal and apoptotic (with or without RIP depletion) HeLa cell extracts were loaded as controls (lanes 1–3). (D) Apoptotic cell extracts were preincubated with 10 μm of DEVD–CHO (lane 4), Z–VAD–FMK (lane 3), or Z–FA–FMK (lane 5) for 15 min, mixed with 35S-labeled RIP protein, and incubated at 30°C for 3 hr. The result was visualized by autoradiograph. The resultant cleavage products are indicated with arrows. The positions of the molecular mass markers are indicated in kD at left of panels.