Figure 3.
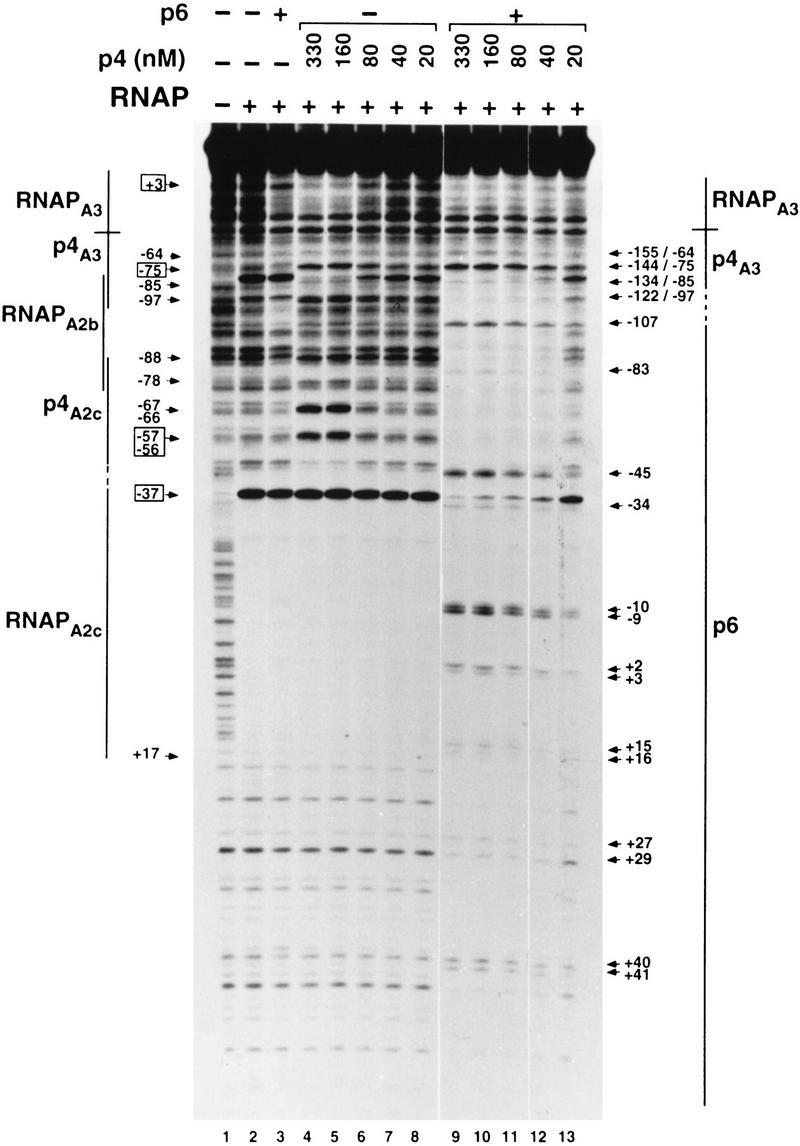
Effect of p6 on the binding of p4 and RNA polymerase to PA2c and PA3. In the reactions with p6, the 366-bp DNA fragment was preincubated with the protein (14.4 μm) for 10 min at 37°C. Protein p4 was present at the indicated concentrations and RNAP at 20 nm. The binding sites for p4, RNAP, and p6 are indicated by lines. Broken lines indicate regions where footprints overlap. Binding of RNAP to PA2c generates hypersensitivity at position −37 and protection from about −55 to +17 (numbered relative to the transcription start site at PA2c). Binding of p4 to PA2c generates the set of hypersensitivities marked above the RNAP-binding site at this promoter. For simplicity, the hypersensitivity at position −82 (relative to the transcription start site at PA3) indicative of RNAP binding to PA2b is not marked. The −64, −75, −85, and −97 hypersensitivities (relative to the transcription start site at PA3) originate from binding of p4 to its site at PA3. Binding of RNAP to PA3 generates protection of a DNA region immediately downstream of the p4-binding site. Arrows at right indicate DNase I hypersensitivities created on binding of protein p6 (numbered relative to the transcription start site at PA2c) and binding of protein p4 to PA3 (numbered relative to the transcription start sites at PA2c/PA3). Numbers in boxes are the specific bands that were densitometrically scanned to obtain data presented in Table 1.
